
Interpretation:
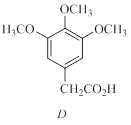
A compound A (C11H14O3) in insoluble in base and gives an isomeric compound B when heated strongly. Compound B gives a sodium salt when treated with NaOH.Treatment of the sodium salt of B with dimethyl sulfate gives a new compound C (C12H16O3) that is identical in all respects to a natural product elemicin.Ozonolysis of elemicin followed by oxidation gives the
Concept introduction:
Sigmatropic reaction can be described as the migration of allylic sigma bond at one end of the π-electron system to the other end of the π-electron system as an uncatalyzed intramolecular reaction. The formation of sigma bond at 3, 3-position of a 1, 5-diene is called as cope rearrangement. Notably, [3, 3] sigmatropic reaction of allyl vinyl ether is termed as Claisen rearrangement.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Quinapril (trade name Accupril) is used to treat high blood pressure andcongestive heart failure. One step in the synthesis of quinapril involvesreaction of the racemic alkyl bromide A with a single enantiomer of theamino ester B. Given the structure of quinapril, which one of these two products isneeded to synthesize the drug?arrow_forwardChemistry (c) Treating lactone B with two equivalents of phenylmagnesium bromide, followed by hydrolysis in aqueous acid, gives a compound with the molecular formula CioHzO, as shown below. Propose a structural formula for this compound. 1. PhMgBr (2 eq.) 2 H'/HO Barrow_forwardThe ketone shown was prepared in a three-step sequence from ethyl trifluoroacetate. The first step in the sequence involved treating ethyl trifluoroacetate with ammonia to give compound A. Compound A was in turn converted to the desired ketone by way of compound B. Fill in the missing reagents in the sequence shown, and give the structures of compounds A and B.arrow_forward
- Compound A of molecular formula C8H₁4 is reduced by sodium in liquid ammonia to give compound of molecular formula C8H16. product (Y). Both A and B undergo hydrogenation in the presence of a platinum catalyst to give 2,5- dimethylhexane. Ozonolysis of B with an oxidative workup produces a carboxylic acid of molecular formula C4H8O2. Reaction of B with a peroxyacid gives a chiral C8H₁40 product, but reaction with bromine gives an achiral C8H₁4Br2 product. What are the identities of A and B? 14 A is 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne; B is cis-2,5-dimethyl-3-hexene A is 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne; B is trans-2,5-dimethyl-3-hexene A is 2,5-dimethyl-1,5-hexadiene; B is 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne A is 2,5-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene; B is cis-2,5-dimethyl-3-hexenearrow_forwardCompound A of molecular formula C8H14 is reduced by sodium in liquid ammonia to give compound B of molecular formula C8H16. product (Y).Both A and B undergo hydrogenation in the presence of a platinum catalyst to give 2,5-dimethylhexane. Ozonolysis of B with an oxidative workup produces a carboxylic acid of molecular formula C4H8O2. Reaction of B with a peroxyacid gives a chiral C8H14O product, but reaction with bromine gives an achiral C8H14Br2 product. What are the identities of A and B?arrow_forward(c) Treating lactone B with two equivalents of phenylmagnesium bromide, followed by hydrolysis in aqueous acid, gives a compound with the molecular formula C18H22O2, as shown below. Propose a structural formula for this compound. 1. PhMgBr (2 eq.) 2. H'/H>O C18H2202 bj 1o 14 10I f6 40 & 3 4 00 (8)arrow_forward
- Each of the following reactions has been carried out under conditions such that disubstitution or trisubstitution occurred. Identify the principal organic product in each case. (a) Nitration of p-chlorobenzoic acid (dinitration) (b) Bromination of aniline (tribromination) (c) Bromination of o-aminoacetophenone (dibromination) (d) Bromination of p-nitrophenol (dibromination) (e) Reaction of biphenyl with tert-butyl chloride and iron(III) chloride (dialkylation) (f) Sulfonation of phenol (disulfonation)arrow_forwardSuggest how you would synthesize each compound, use cyclopentanone as one of the reagentsarrow_forwardLinalool and lavandulol are two of the major components of lavender oil. (a) What organolithium reagent and carbonyl compound can be used to make each alcohol? (b) How might lavandulol be formed by reduction of a carbonyl compound? (c) Why can't linalool be prepared by a similar pathway?arrow_forward
- Octinoxate is an unsaturated ester used as an active ingredient in sunscreens. (a) What carbonyl compounds are needed to synthesize this compound using a condensation reaction? (b) Devise a synthesis of octinoxate from the given organic starting materials and any other needed reagents.arrow_forwardThe following questions pertain to the esters shown and behavior under conditions of the Claisen condensation.(a) Two of these esters are converted to β-keto esters in good yield on treatment with sodium ethoxide and subsequent acidification of the reaction mixture. Which two are these? Write the structure of the Claisen condensation product of each one. (b) One ester is capable of being converted to a β-keto ester on treatment with sodium ethoxide, but the amount of β-keto ester that can be isolated after acidification of the reaction mixture is quite small. Which ester is this? (c) One ester is incapable of reaction under conditions of the Claisen condensation. Which one? Why?arrow_forwardCompound A has molecular formula C7H15B.. Treatment of compound A with sodium ethoxide yields only one elimination product (compound B) and no substitution products. When compound B is treated with dilute sulfuric acid, compound C is obtained, which has molecular formula C7H160. Draw the structures of compounds A, B, and C.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole


