
(a)
Interpretation: The major organic product that would result from reaction should be identified.
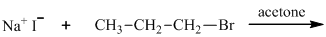
Concept introduction:
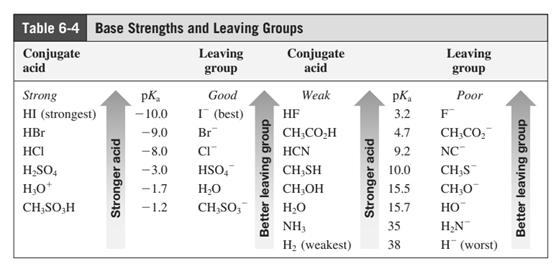
Leaving-group ability is determined by the capacity of leaving group to accommodate the negative charge as it is displaced from the alkyl halide. Among halogens, the iodides are best-leaving groups followed by bromide chloride and fluoride. Besides halides, some sulphonates and sulphate that can easily delocalize the negative charge can also behave as good leaving group. These include tosylate, mesylate and triflate.
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. The table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases is as follows:
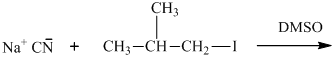
(b)
Interpretation: The structure of major organic product that would result from below reaction of should be written.
Concept introduction:
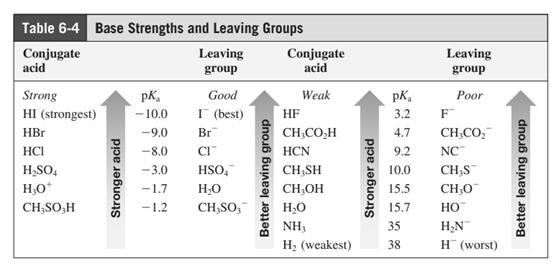
Leaving-group ability is determined by the capacity of leaving group to accommodate the negative charge as it is displaced from the alkyl halide. Among halogens, the iodides are best-leaving groups followed by bromide chloride and fluoride. Besides halides, some sulphonates and sulphate that can easily delocalize the negative charge can also behave as good leaving group. These include tosylate, mesylate and triflate.
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. The table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases is as follows:
(c)
Interpretation: The structure of major organic product that would result from reaction of should be written.
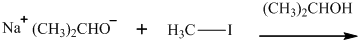
Concept introduction:
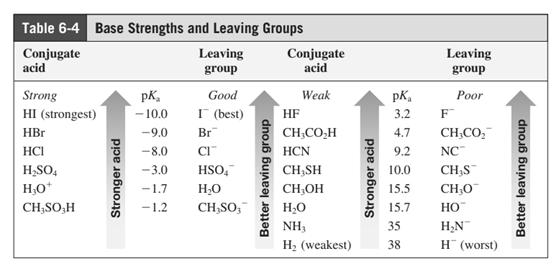
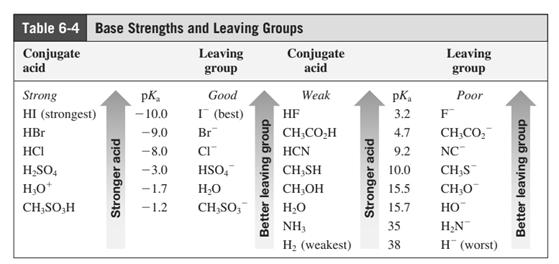
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. The table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases is as follows:
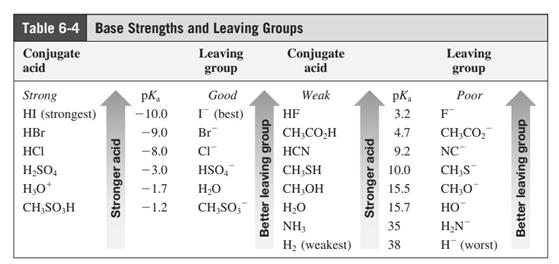
(d)
Interpretation: The structure of major organic product that would result from below reaction of should be written.
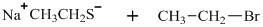
Concept introduction:
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. The table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases is as follows:
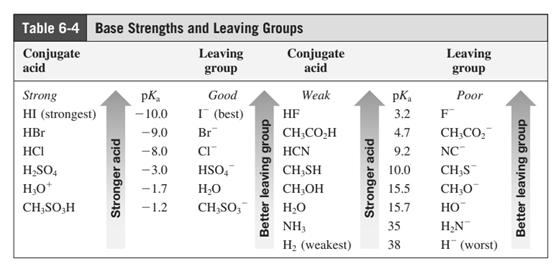
(e)
Interpretation: Product that would result from bimolecular substitution reaction should be written.
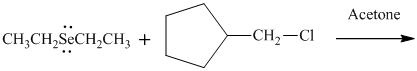
Concept introduction:
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. The table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases is as follows:
(f)
Interpretation: The structure of major organic product that would result from reaction of should be written.
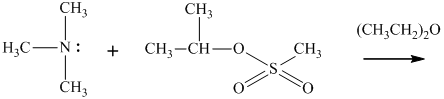
Concept introduction:
In general, the weak conjugate bases that are derived from strong acids are also good leaving groups. The table for leaving groups on the basis of strength of bases is as follows:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Write down the common (not IUPAC) names of the organic molecules that would be released if this molecule were hydrolyzed: о CH2-0-C-(CH2)7-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-(CH2)4-CH3 CH о O-C-(CH2)7-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-CH3 CH2-O-C-(CH2)4-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-(CH2)4-CH3 Separate each name with a comma. You will find useful information in the ALEKS Data resource.arrow_forwardWrite down the common (not IUPAC) names of the organic molecules that would be released if this molecule were hydrolyzed: о CH2 O-C-(CH2)7-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-(CH2)4-CH3 о CH-O-C-(CH2)7-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-CH3 CH2 O-C-(CH2)4-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-(CH2)4-CH3 Separate each name with a comma. You will find useful information in the ALEKS Data resource.arrow_forwardThe acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2,3-dimethyl-3-pentanol yields three alkene products. What are the names of the three alkenes? Which of the three alkenes is the major product?arrow_forward
- Which of the following chemical equations depicts an alkylation reaction? C6H6() + CH3Cl() → C6H5CH3() + HCl(g) 2 CH3OH() + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 4 H2O() C6H12() → C6H10() + H2(g) CH2ClCH2Cl(g) + H2(g) → CH3CH3(g) + Cl2(g) CHClCHCl(g) → CH2ClCH2Cl(g)arrow_forwardButene (CH2CHCH2CH3) reacts with hydrogen chloride (HCl) at room temperature. Draw the displayed formulae of the products formed in this reaction. State the name of the above reaction mechanism. Alkene Propene reacts with hydrogen bromide (HBr) at room temperature to produce, 1-bromopropane and 2-bromopropane. H2C=CHCH3 + HBr → CH2(Br)CH2CH3 + CH3CH(Br)CH3 Draw out the reaction mechanism of the reaction between propene and hydrogen bromide to produce 2-bromopropane. Use curly arrows to show the movement of electrons. The description should be detailed and must include the type of bond fission that takes place. You may sketch and insert suitable diagrams to aid your description if you wish. Referring to the above mechanism, explain why two products are formed…arrow_forwardWrite the structure of the compound that will be produced in the following reaction? CH3 –C ≡ C–CH2– CH2 – CH3 + 2HBr→arrow_forward
- [Review Topics] [References] Draw the structure(s) of the major organic product(s) of the following reaction. 우 + 1 eq. Cl₂ Aqueous NaHCO3 0° Carrow_forwardGive the IUPAC name of the product that would form when the following alkene undergoes catalytic hydrogenation. CH, CH=CHCHCH, Name of product !3!arrow_forwardDraw a structural formula for the major organic product of the reaction shown. CH3CH2 CH,CH,CH3 C=C HI H H.arrow_forward
- Draw the organic product you would expect to isolate from the nucleophilic substitution reaction between the molecules shown. Note: You do not need to draw any of the side products of the reaction, only the substitution product. + H₂O Cl + ☑ 5 C Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWhich alcohols can be prepared as a single product by hydroboration– oxidation of an alkene? Which alcohols can be prepared as a single product by the acid-catalyzed addition of H2O to an alkene?arrow_forwardWhich alcohols can be prepared as a single product by hydroboration–oxidation of an alkene? Which alcohols can be prepared as a singleproduct by the acid-catalyzed addition of H2O to an alkene?arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
