
Evolutionary Analysis (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780321616678
Author: Jon C. Herron, Scott Freeman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 10Q
Referring to the information in Figure 4.10, explain why the bones found in bird wings and bat wings are homologous. Then explain why the use of the forelimb for powered flight is a convergent trait in birds and bats.
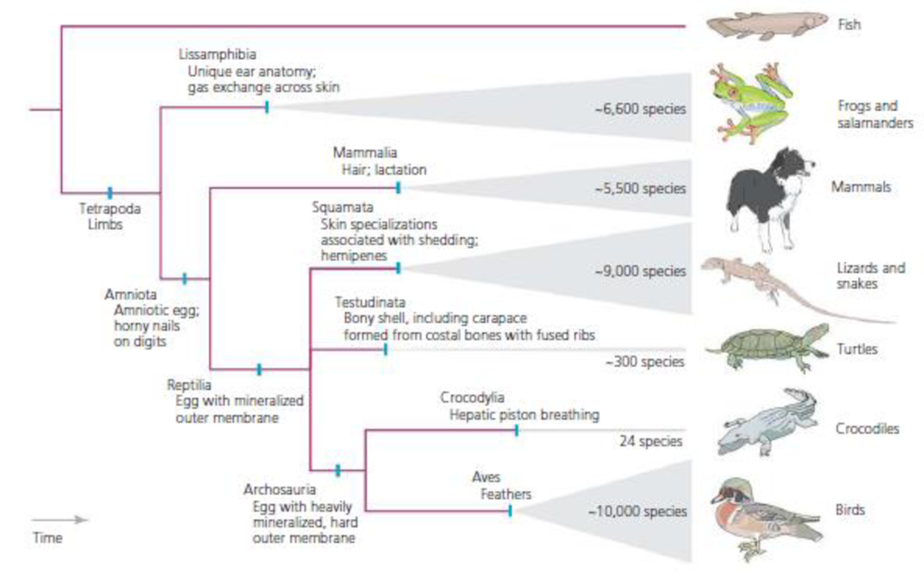
Figure 4.10 Major monophyletic groups of tetrapods Gray triangles at branch tips represent diversifications within monophyletic groups that could, space permitting, be represented by multifarious evolutionary trees. Based on Gans and Clark (1976), Meylan (2001), Alibardi and Maderson (2003), Kearney (2003), Mindell and Brown (2005), Carroll (2007), Laurin and Reisz (2007), Claessens (2009), Hoffmann et al. (2010), Laurin (2011), and Laurin and Gauthier (2011).
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
4
05
4
3.
2.
D.
Using the terms listed below, answer all the parts to this question regarding the cladogram for the frogs
Anatomy of a Cladogram
Sympleisiomorphies—shared ancestral states
Synapomorphies—shared, derived character states
Autapomorphies—unique, derived character states
Homoplasies—the result of parallel or convergent evolution where 2 or more organisms independently acquire the same character state (could be the result of a reversal—when, in a particular lineage, a character reverts from a derived back to an ancestral state). Similarity in appearance, but not origin.
Monophyletic group—group of all descendants of a common ancestor
Paraphyletic group—group of some, but not all, descendants of a common ancestor
Polyphyletic group – group of individuals that descend from more than one common ancestor
Polytomy—3 or more taxa emerging from a single node who do not share the most common ancestor
Homologies—Similarities resulting from descent from a common ancestor
Analogies - Similarities…
Using the terms listed below, answer all the parts to this question regarding the cladogram for the frogs
Anatomy of a Cladogram
Sympleisiomorphies—shared ancestral states
Synapomorphies—shared, derived character states
Autapomorphies—unique, derived character states
Homoplasies—the result of parallel or convergent evolution where 2 or more organisms independently acquire the same character state (could be the result of a reversal—when, in a particular lineage, a character reverts from a derived back to an ancestral state). Similarity in appearance, but not origin.
Monophyletic group—group of all descendants of a common ancestor
Paraphyletic group—group of some, but not all, descendants of a common ancestor
Polyphyletic group – group of individuals that descend from more than one common ancestor
Polytomy—3 or more taxa emerging from a single node who do not share the most common ancestor
Homologies—Similarities resulting from descent from a common ancestor
Analogies - Similarities…
Chapter 4 Solutions
Evolutionary Analysis (5th Edition)
Ch. 4 - According to the evolutionary tree in Figure 4.37,...Ch. 4 - According to the evolutionary tree in Figure 4.37,...Ch. 4 - Sketch a version of the tree in Figure 4.37 in...Ch. 4 - In the tree in Figure 4.37, identify a...Ch. 4 - What is a synapomorphy?Ch. 4 - High-crowned teeth that are well suited for...Ch. 4 - Assuming the four living species in Figure 4.38...Ch. 4 - The four fish in Figure 4.39 evolved from a common...Ch. 4 - What is homoplasy? Why does homoplasy make it more...Ch. 4 - Referring to the information in Figure 4.10,...
Ch. 4 - What is the difference between a molecular...Ch. 4 - Why is it seldom possible to exhaustively check...Ch. 4 - A clade in a phylogeny bears a label at its base...Ch. 4 - Examine the three primate phylogenies shown in...Ch. 4 - Historically, some scientists hypothesized that...Ch. 4 - Sketch the tree you would expect for dogs, wolves,...Ch. 4 - Darwin maintained that among living species, there...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The phylogenetic tree for vertebrates depicted below was constructed from sequence data for two rRNA mitochondrial genes (12S and 16S). How do the results of this analysis compare with the phylogenetic trees in Figures 32.10 and 32.24? Identify the major clades of vertebrates on the tree depicted below. Source: R. Zardoya and A. Meyer. 1998. Complete mitochondrial genome suggests diapsid affinities of turtles. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 95:1422614231. Copyright 1998 National Academy of Sciences, U.S.A.arrow_forwardA 2015 article in Nature has summarized the early history of jawed vertebrates using highlights from recent discoveries and how they have changed our understanding of vertebrate evolution. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2014/04/140416133336.htm Question: Given these recent discoveries, how should the cladogram below change? Describe it. It will likely be helpful to reference a synapomorphy noted on the cladogram.arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions about this phylogenetic tree. What animal represents the out group in this tree and why? What is the derived characteristic of the birds? What is the shared characteristic of 3 to 6? Which number represents the common ancestor of Ostriches and Hawks?arrow_forward
- Draw a phylogenetic reconstruction for the hypothetical frog species. Once you have a cladogram you feel confident about, use lines and labels on cladogram to indicate where character states hanged. How many evolutionary changes occurred in your phylogeny? Is there evidence of an evolutionary convergence having occurred in your phylogeny? How about evolutionary reversals?arrow_forward5. 5. Draw a phylogeny the following taxa: shark; tuna; frog; lizard; mouse; whale. On your phylogeny label the first occurrence/evolution of the following traits: cartilaginous skeleton; bony skeleton; hair; four limbs; shelled eggs. Describe a synapomorphy using any of the traits you labeled on the tree.arrow_forwardThe tree below shows a proposed phylogeny of the three broadest mammal groups. monotremes marsupials eutherians Figure 1: Phylogenetic relationsbips between defrent ypes of mammals. a. Which group of mammals branched off the earliest? b. Which letter designates the common ancestor to monotremes and marsupials? c. Indicate where on the tree (short perpendicular line) each of the following characters arose. 1. long-lived placenta 4. internal gestation (rather than in egg) 2. body hair 5. long-term gestation 3. production of milk for young 6. live birth (rather than egg laying e. Which of the above characters are shared ancestral characters of eutherians? List all that apply.arrow_forward
- In the late 1800's, a biologist studying animal embryos coined the phrase, "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny", meaning that the physical development of an animal embryo (ontogeny) seemed to retrace the changing form of the species during its evolutionary history (phylogeny). Why would embryonic development retrace evolutionary steps?arrow_forwardA study inferred a maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on sequence data from a specific gene. Numbers represent bootstrap support values for each clade. Based on the study's findings, how certain should we be that marsupials are sister to placental mammals, rather than monotremes? What number is used to represent this certainty, and how was it calculated?arrow_forwardFor each statement about the trees shown below, indicate whether it is TRUE (1) or FALSE (2). These trees show that there are far more species of tetrapods (vertebrates with four limbs) than there are of bony fishes. Only tree 1 is accurate because it shows humans, the most complex species, at one end and fishes, the simplest lineage, at the other end. Humans and lizards are equally closely related to frogs according to both trees. The only difference between these two trees is that some of the internal nodes have been rotated. They show the same topology and therefore represent the same evolutionary relationships. The lineage represented by fishes has been evolving for a much longer time than the lineage represented by lizards.arrow_forward
- In the past, the evolutionary history of whales was represented by cladogram A, shown below. As you can see, whales were believed to be closely related to mesonychids, an extinct group of mammals that looked similar to wolves. Today, that cladogram has been revised, as shown in cladogram B. Cladogram A Cladogram B Hippos Horses Hippos Whales Ruminants Pigs Camels Horses Mesonychids Time Time Which of the following statements best describes the reason for this change? Cladograms A and B are hypotheses that changed as new evidence became available. Cladogram B was revised to show a water-to-land pattern of evolution in groups of organisms. Cladogram B was altered to better include similarities in habitat as new information became available. Cladograms are organized today to show a much more simplified pattern like the one shown in cladogram B.arrow_forwardA bat wing and a cat paw have different functions but similar bones and development. Which term best describes the bat wing and cat paw (both are mammals)? Question options: Embryological structures Analogous structures Homologous structures Genealogical structures Which of the following is probably the best explanation for the fact that Antarctic penguins cannot fly, although there is evidence that millions of years ago their ancestors could Question options: The Antarctic home of penguins is flat and barren; therefore there is no place to fly. Ancestral penguins without large wings were better able to swim and feed in the water; therefore they passed their genes for shorter wings structure onto their offspring. Ancestral penguins did not use their wings for long periods of time; therefore today’s penguins have only tiny, nonfunctional wings. The cold and wind of Antarctica make flight impossible; therefore penguins that live…arrow_forwardBased on the phylogenetic tree diagram in Figure 34.2, predict which vertebrate groups should have lungs or lung derivatives. Explain.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Fossils & Evidence For Evolution | Evolution | Biology | FuseSchool; Author: FuseSchool - Global Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iYr3sYS9e0w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Dig In To Paleontology; Author: SciShow Kids;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1FjyKmpmQzc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY