
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The types of carbonyl group in the given molecule should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Carbonyl group:
A carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom
If the carbonyl carbon is attached with two alkyl or aryl group is called as ketone, if the carbonyl carbon is attached with one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group is called as aldehyde.
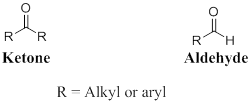
One
Carboxylic acid can be represented as,
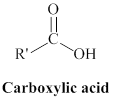
The derivatives of carboxylic acid are ester, amide.
One
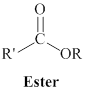
One
Amides can be represented as,
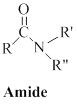
(b)
Interpretation:
The carbonyl group in the given molecule should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which are determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
Carbonyl group:
A carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom
If the carbonyl carbon is attached with two alkyl or aryl group is called as ketone, if the carbonyl carbon is attached with one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group is called as aldehyde.
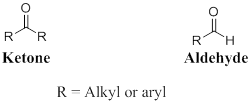
One
Carboxylic acid can be represented as,

The derivatives of carboxylic acid are ester, amide.
One
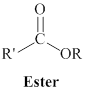
One
Amides can be represented as,

(c)
Interpretation:
The carbonyl group in the given molecule should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which are determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
Carbonyl group:
A carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom
If the carbonyl carbon is attached with two alkyl or aryl group is called as ketone, if the carbonyl carbon is attached with one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group is called as aldehyde.
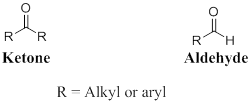
One
Carboxylic acid can be represented as,

The derivatives of carboxylic acid are ester, amide.
One
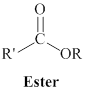
One
Amides can be represented as,

(d)
Interpretation:
The carbonyl group in the given molecule should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which are determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
Carbonyl group:
A carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom
If the carbonyl carbon is attached with two alkyl or aryl group is called as ketone, if the carbonyl carbon is attached with one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group is called as aldehyde.
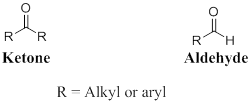
One
Carboxylic acid can be represented as,

The derivatives of carboxylic acid are ester, amide.
One
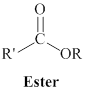
One
Amides can be represented as,

(e)
Interpretation:
The carbonyl group in the given molecule should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which are determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
Carbonyl group:
A carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom
If the carbonyl carbon is attached with two alkyl or aryl group is called as ketone, if the carbonyl carbon is attached with one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group is called as aldehyde.
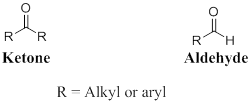
One
Carboxylic acid can be represented as,

The derivatives of carboxylic acid are ester, amide.
One
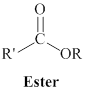
One
Amides can be represented as,

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
General Chemistry: Atoms First
- Glucose, C6H12O6, contains an aldehyde group but exist predominantly in the form of the cyclic hemiacetal show below. A cyclic hemiacetal is formed when the —OH group of one carbon bonds to the carbonyl group of another carbon. Identify which carbon provides the —OH group and which provides the —CHO? Give a functional isomer of glucose and draw its structure.arrow_forward(a) Is C4H6 a saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbon?(b) Are all alkynes unsaturated?arrow_forwardGive the structural formulae and name the functional groups of the following compounds. (a) 3-chlorobut-1-ene Name the functional group: (b) butanedioic acid Name the functional group: (c) propanamide Name the functional group: (d) 3-methylbutanal Name the functional group:arrow_forward
- The foul odor of rancid butter is caused by butyric acid, CH3CH2CH2CO2H.(a) Draw the Lewis structure and determine the oxidation number and hybridization for each carbon atom in the molecule.(b) The esters formed from butyric acid are pleasant-smelling compounds found in fruits and used in perfumes. Draw the Lewis structure for the ester formed from the reaction of butyric acid with 2-propanol.arrow_forward(a) Which of the following compounds, if any, is an ether? (b) Which compound, If any, is an alcohol? (c) Which com- pound, if any, would produce a basic solution if dissolved in water? (Assume solubility is not a problem). (d) Which compound, if any, is a ketone? (e) Which compound, if any, is an aldehyde? () Н,С—CH;—он Н (ii) H;C-Ñ-CH,CH=CH2 (ii) o (iv) (v) CH;CH,CH,CH2CHO (vi) CH3C=CCH,COOHarrow_forward5. Give the structural formulae and name the functional groups of the following compounds. (a) 3-chlorobut-1-ene (b) butanedioic acid Name the functional group: (c) propanamide Name the functional group: (d) 3-methylbutanal Name the functional group: Name the functional group:arrow_forward
- A certain hydrocarbon has a molecular formula of C5H8. Which of the following is not a structural possibility for this hydrocarbon: (d) It contains an alkyne O It contains one ring and one double bond (c) It contains two double bonds and no rings O (b) It contains one ring and no double bondsarrow_forwardThe ester with the formula C8H16O2 gives an alcohol and an acid when hydrolyzed. When the alcohol is isolated and oxidized, it forms a ketone. Which of these formulas cannot be the ester?arrow_forwardGive the IUPAC names of structures containing two carbon atoms for the following classes of compounds: (a) ether: (b) aldehyde: (c) carboxylic acid: (d) ester:arrow_forward
- Draw condensed structural formulas for all compounds with the molecular formula C4H8O that contain a carbonyl group (there are two aldehydes and one ketone).arrow_forward5.Write the structural formula of the ester that, when hydrolyzed, would yield the following:(a) methanol and propanoic acid(b) 1-octanol and acetic acid (c) ethanol and butanoic acidarrow_forward(B) Draw a structural diagram for each of the following organic compounds: (a) 2-ethyl-4-methyl-2-pentanol (b) 1,2-ethandiol (c) 1,3-dimethylbenzenearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





