
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Valence bond description of the bonding in the given compound has to be given along with its orbital diagram for the free metal ion and metal ion in the complex. The hybrid orbitals which are used by the metal ion for bonding should be indicated and the number of unpaired electron should be specified.
Concept introduction:
Coordination compounds are a special class of compounds in which the metal atoms or ions are bounded to a number of anions or neutral molecules.
A coordination compound can be simply represented as follows,
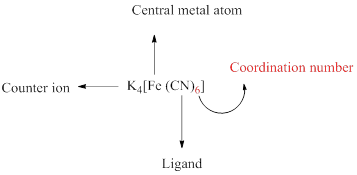
Coordination number of a complex is defined as the number of ligand donor atoms to which the metal is directly bonded.
According to
These hybridized orbitals are allowed to overlap with ligand orbitals that can donate electron pairs for bonding.
Inner orbital complex are coordination compounds having a central metal atom that undergoes hybridization of atomic orbital including the inner d (
Outer orbital complex are coordination compounds having a central metal atom that undergoes hybridization of atomic orbital including the outer most d (
(b)
Interpretation:
Valence bond description of the bonding in the given compound has to be given along with its orbital diagram for the free metal ion and metal ion in the complex. The hybrid orbitals which are used by the metal ion for bonding should be indicated and the number of unpaired electron should be specified.
Concept introduction:
Coordination compounds are a special class of compounds in which the metal atoms or ions are bounded to a number of anions or neutral molecules.
A coordination compound can be simply represented as follows,

Coordination number of a complex is defined as the number of ligand donor atoms to which the metal is directly bonded.
According to valence bond theory, the metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands can use its
These hybridized orbitals are allowed to overlap with ligand orbitals that can donate electron pairs for bonding.
Inner orbital complex are coordination compounds having a central metal atom that undergoes hybridization of atomic orbital including the inner d (
Outer orbital complex are coordination compounds having a central metal atom that undergoes hybridization of atomic orbital including the outer most d (
(c)
Interpretation:
Valence bond description of the bonding in the given compound has to be given along with its orbital diagram for the free metal ion and metal ion in the complex. The hybrid orbitals which are used by the metal ion for bonding should be indicated and the number of unpaired electron should be specified.
Concept introduction:
Coordination compounds are a special class of compounds in which the metal atoms or ions are bounded to a number of anions or neutral molecules.
A coordination compound can be simply represented as follows,

Coordination number of a complex is defined as the number of ligand donor atoms to which the metal is directly bonded.
According to valence bond theory, the metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands can use its
These hybridized orbitals are allowed to overlap with ligand orbitals that can donate electron pairs for bonding.
Inner orbital complex are coordination compounds having a central metal atom that undergoes hybridization of atomic orbital including the inner d (
Outer orbital complex are coordination compounds having a central metal atom that undergoes hybridization of atomic orbital including the outer most d (
(d)
Interpretation:
Valence bond description of the bonding in the given compound has to be given along with its orbital diagram for the free metal ion and metal ion in the complex. The hybrid orbitals which are used by the metal ion for bonding should be indicated and the number of unpaired electron should be specified.
Concept introduction:
Coordination compounds are a special class of compounds in which the metal atoms or ions are bounded to a number of anions or neutral molecules.
A coordination compound can be simply represented as follows,

Coordination number of a complex is defined as the number of ligand donor atoms to which the metal is directly bonded.
According to valence bond theory, the metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands can use its
These hybridized orbitals are allowed to overlap with ligand orbitals that can donate electron pairs for bonding.
Inner orbital complex are coordination compounds having a central metal atom that undergoes hybridization of atomic orbital including the inner d (
Outer orbital complex are coordination compounds having a central metal atom that undergoes hybridization of atomic orbital including the outer most d (
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 20 Solutions
General Chemistry: Atoms First
- Four different octahedral chromium coordination compounds exist that all have the same oxidation state for chromium and have H2O and Cl as the ligands and counterions. When 1 mole of each of the four compounds is dissolved in water, how many moles of silver chloride will precipitate upon addition of excess AgNO3?arrow_forwardPlatinum(II) forms many complexes, among them those with the following ligands. Give the formula and charge of each complex. (a) two ammonia molecules and one oxalate ion (C2O42-) (b) two ammonia molecules, one thiocyanate ion (SCN-), and one bromide ion (c) one ethylenediamine molecule and two nitrite ionsarrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning





