
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
The compounds which have the same molecular formula but have different arrangements of atoms are known as isomers. The phenomenon is called isomerism. The isomers are generally classified as structural isomers and stereoisomers. Stereoisomers are further divided into two categories diastereomers and enantiomers.
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The isomers of
Explanation of Solution
The structures of
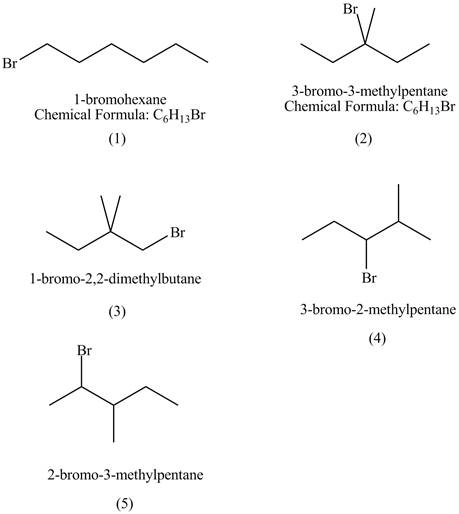
Figure 1
The compounds that have chiral centers can exist as enantiomers. The compound
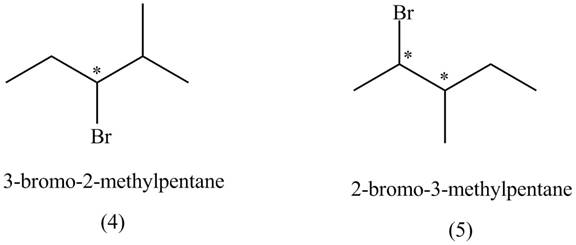
Figure 2
Therefore,
The compounds
(b)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halides among
Concept introduction:
The compounds which have the same molecular formula but have different arrangements of atoms are known as isomers. The phenomenon is called isomerism. The isomers are generally classified as structural isomers and stereoisomers. Stereoisomers are further divided into two categories diastereomers and enantiomers.
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The isomer of
Explanation of Solution
The structures of
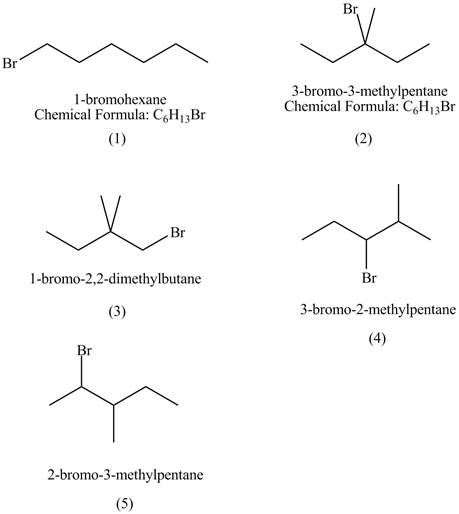
Figure 1
The compounds that have two chiral centers can exist as enantiomers. The compound
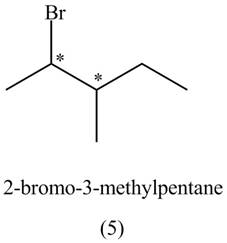
Figure 3
Therefore,
The compound
(c)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halides among
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as a substitution reaction. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving the group by attacking on the electron-deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The fastest
Explanation of Solution
The structures of
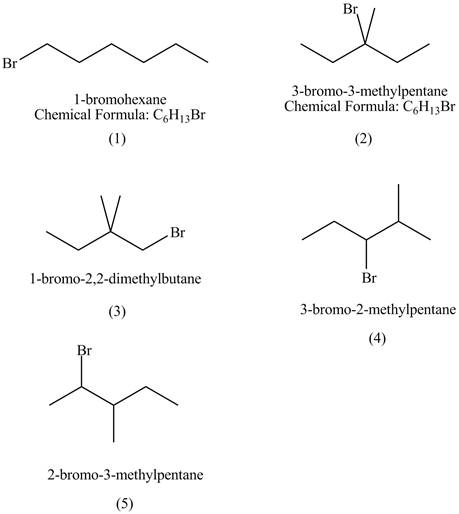
Figure 1
The rate of
The compound
The compound
(d)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halides among
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The isomer of
Explanation of Solution
The structures of

Figure 1
The compound
The compound,
(e)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halides among
Concept introduction:
The elimination reaction of alkyl halide involves removal of the halogen atom and hydrogen atom from the adjacent carbon atoms, which leads to the formation of the alkene. A bulky base increases the chance of elimination reaction of substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The compound
Explanation of Solution
The structures of
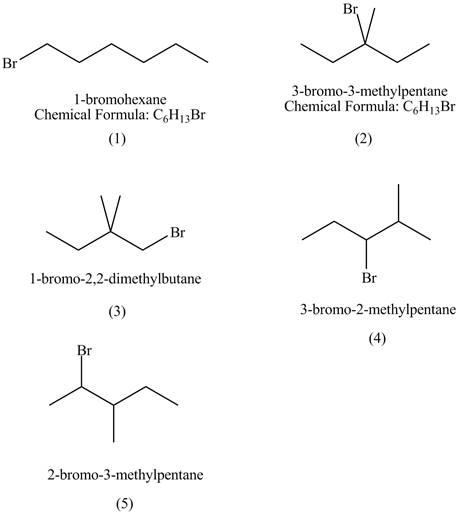
Figure 1
The compound
The
(f)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halides among
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as a substitution reaction. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving the group by attacking on the electron-deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The alkyl halide among
Explanation of Solution
The structures of
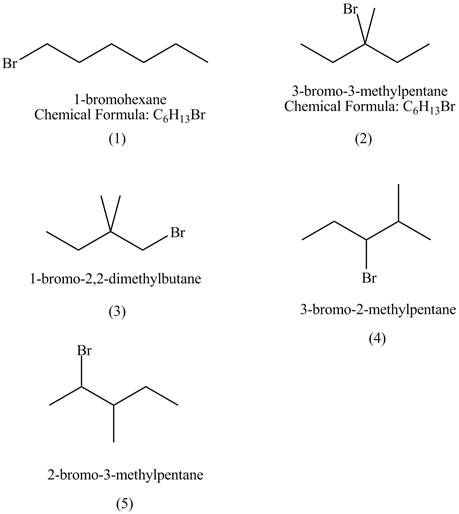
Figure 1
The rate of
The steric hindrance in case of
The isomer of
(g)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halides among
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as a substitution reaction. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving the group by attacking on the electron-deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The alkyl halides among
Explanation of Solution
The structures of

Figure 1
The stability of tertiary carbocation is more than the stability of secondary carbocation. Therefore, in case of
The isomer of
(h)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide among
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as a substitution reaction. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving the group by attacking on the electron-deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 9.44AP
The alkyl halide among
Explanation of Solution
The structures of

Figure 1
The rate of
Therefore,
The isomer of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- There are 17 possible alkene isomers with the formula C6H12. Draw structures of the five isomers in which the longest chain has six carbon atoms, and give the name of each. Are any of these isomers chiral? (There are also eight isomers in which the longest chain has five carbon atoms, and four isomers in which the longest chain has four carbon atoms. How many can you find?)arrow_forwardDraw the structural formula for each of the following compounds:(i) 3-methyl-5-(2,2-dimethylpropyl) nonane(ii) 1,2-dichloro-3-methylcyclohexanearrow_forwardThere are two alkenes that react with HBr to give 1-bromo-1-methylcyclohexane. Draw their structures.arrow_forward
- The reaction of Hbr with 2-methylpropene produces 2-bromo-2-methylpropane. What is the structure of the carbocation formed during the reaction?arrow_forwardamidal trigonal pyramidal tetrahedral trigonal pyramidal (D) 6 n this ACS -6-ethyl-7-methyl-3-octene 5. Which structure has the IUPAC name 2-ethyl-5-methylhexan-1-ol? (A) (B) (C) (D) (A) HO (C) HO OH 6. Which is the most stable carbocation? H OH octene (B) (D) OCH 3 500arrow_forwardName the following molecule. CH₂CH3 H-CH3 H3C H Br (2R, 3R)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane (2S,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane O (2R,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane (1R, 2S)-1-bromo-1,2-dimethylbutane (1S,2R)-1-bromo-1,2-dimethylbutanearrow_forward
- Classify each of the following reactions as a substitution, elimination or addition reaction: Br Нeat (a) Br2 + HBr Br CN (b) + CN + Br Br (c) + Br2 Brarrow_forward3. The following alkenes can be prepared by dehydration of an appropriate alcohol. Show the structure of the alcohol in each case. If the alkene can arise from dehydration of more than one alcohol, show all possibilities. CH3CH2 C=CH2 CH3CH2 a) сH-с—снCH,CHз CH3 b) c) 3-hexene d) 1,3-butadienearrow_forward5. What is the IUPAC name of the following molecule? Br (a) 2-bromo-4-isopropyl-3-methylbutane (b) 2-bromo-3,5-dimethylhexane (c) 3,4-dimethyl-2-bromohexane (d) 2-bromo-3-methyl-4-propylbutane (e) 2-bromo-3,5-dimethylheptanearrow_forward
- 9. The following picture which illustrates the overlap of 2p orbitals to form the T-bonds of an alkyne clearly shows that the angle of the o-bonds must be (a) 120°, (b) 180°, (c) 109.5°. (d) 60° TT H. TT 10. What is the correct name for the following alkyne? (a) 2-chloro-6-methyl-4-heptyne (b) 6-chloro-2-pethyl-3-heptyne (c) 4-chloro-1-isopropyl-1-pentyne (d) isopropyl 2-chloropropyl acetylene CI 11. Select the structure which corresponds to the name 1-methyl-1,3,5-cyclooctatriene (а) (b) (c) (d)arrow_forwardHow many tertiary alkyl halides have the formula C4H9BR? (А) 3 B 1 C 2 D 4arrow_forwardc) For the IUPAC names below, provide an unambiguous structure! 1) (1R, 2R, 4S)-1,2-dibromo-4-methyl-cyclohexane 2) (2R, 3Z)-5-Fluoro-3-penten-1,2-diolarrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


