
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The ratio of A- to [HA] with the help of pH and pKa values should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
The pH of a solution indicates the number of H3 O+ ions in the solution. The mathematical relation between pH and H3 O+ is as given below;.
Acid dissociation constant Ka is related to pKa as;.
Answer to Problem 30P
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
pKa = 5.0.
pH = 2.0.
Calculation:
From pH of solution, concentration of hydroxide ion can be calculated as follows:
Also,
Since,
Thus, by putting the values, the ratio
(b)
Interpretation:
The ratio of A- to [HA] with the help of pH and pKa values should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
The pH of a solution indicates the number of H3 O+ ions in the solution. The mathematical relation between pH and H3 O+ is as given below;.
Acid dissociation constant Ka is related to pKa as;.
Answer to Problem 30P
Given:
pKa = 5.0.
pH = 5.0.
Hence [H3 O+ ] = 10-pH = 10-5.
And Ka = 10-pKa = 10-5.
Since 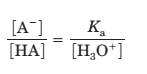
Plug the values of Ka and H3 O+ ions to calculate the ratio of [A- ] to [HA].
[A- ] / [HA] = 10-5 / 10-5 = 1.
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
pKa = 5.0.
pH = 5.0.
Calculation:
From pH of solution, concentration of hydroxide ion can be calculated as follows:
Also,
Since,
Thus, by putting the values, the ratio
(c)
Interpretation:
The ratio of A- to [HA] with the help of pH and pKa values should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
The pH of a solution indicates the number of H3 O+ ions in the solution. The mathematical relation between pH and H3 O+ is as given below;.
Acid dissociation constant Ka is related to pKa as;.
Answer to Problem 30P
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
pKa = 5.0.
pH = 7.0.
Calculation:
From pH of solution, concentration of hydroxide ion can be calculated as follows:
Also,
Since,
Thus, by putting the values, the ratio
(d)
Interpretation:
The ratio of A- to [HA] with the help of pH and pKa values should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
The pH of a solution indicates the number of H3 O+ ions in the solution. The mathematical relation between pH and H3 O+ is as given below;.
Acid dissociation constant Ka is related to pKa as;.
Answer to Problem 30P
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
pKa = 5.0.
pH = 9.0.
Calculation:
From pH of solution, concentration of hydroxide ion can be calculated as follows:
Also,
Since,
Thus, by putting the values, the ratio
(e)
Interpretation:
The ratio of A- to [HA] with the help of pH and pKa values should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
The pH of a solution indicates the number of H3 O+ ions in the solution. The mathematical relation between pH and H3 O+ is as given below;.
Acid dissociation constant Ka is related to pKa as;.
Answer to Problem 30P
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
pKa = 5.0.
pH = 11.0.
Calculation:
From pH of solution, concentration of hydroxide ion can be calculated as follows:
Also,
Since,
Thus, by putting the values, the ratio
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Introduction To General, Organic, And Biochemistry
- Determine the pH of each of the following solutions.(a) 0.257 M hypobromous acid (weak acid with Ka = 2.5e-09).(b) 0.809 M ascorbic acid (weak acid with Ka = 8e-05).(c) 0.555 M pyridine (weak base with Kb = 1.7e-09).arrow_forwardA 0.20 M solution of niacin has a pH of 3.6. (a) What percentage of the acid is ionized in this solution? (b) What is the Ka for niacin?arrow_forward(f) Calculate the pH of the following solutions: (i) A 0.045 M solution of sulphuric acid. (ii) A solution containing 0.4 g sodium hydroxide in 100 cm³ water. (iii) Given the Ka value for CH3COOH is 1.8 x 10-5, calculate the pH of the acid. The initial concentration of the acid is 0.2 Marrow_forward
- The pH reading of a sample of each substance is given. Calculate the hydrogen ion concentration of the substance. (Give your answers in scientific notation, correct to one decimal place.) (a) Vinegar: pH = 3 %3D [H+] = x 10 M (b) Crackers: pH = 7.2 %3D [H+] = x 10 M (p ツarrow_forwardCalculate the pKa of the weak acid HA, given that a solution of 0.65 M HA and 0.85 M NaA has a pH of 4.75arrow_forwardDetermine the pH of each of the following solutions.(a) 0.684 M hypochlorous acid (weak acid with Ka = 3e-08).(b) 0.399 M hydrogen peroxide (weak acid with Ka = 2.4e-12).(c) 0.751 M pyridine (weak base with Kb = 1.7e-09).arrow_forward
- 8. (a) Calculate the percent ionization of a 0.20 M solution of the monoprotic acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) for which Ka = 3.0 x 10-4 .(b)The pH of gastric juice in the stomach of a certain individual is 1.00. After a few aspirin tablets have been swallowed, the concentration of acetylsalicylic acid in the stomach is 0.20M. Calculate the % ionization of the acid under these conditions. What effect does the nonionized acid have on the membranes lining of the stomach? 9. Calculate the [H+], [C2O4-2], and [H2C2O4] in a 0.0010M H2C2O4 solution. (Ka = 5.4 x 10-2)arrow_forward4. (a) Calculate [H3O*] and [OH] for the solutions indicated: lemon juice, pH = 2.42 (1) (ii) household ammonia pH = 11.21 (iii) (iv) (v) phosphate buffer pH = 6.96 human urine pOH = 7.8 tomato juice pOH = 9.9arrow_forwardWhat is the conjugate base of boric acid, B(OH)3? (A) OH– (B) B(OH)4– (C) B(O)(OH)22– (D) B(H2O)(OH)2+arrow_forward
- Hypochlorous acid, HOCl, is a weak acid having a pKa = 7.46. (a) Show the balanced chemical equation for the hydrolysis of water by OCl- (aq). (b) Compute the value of pKb for aqueous hypochlorite ion. (c) If [OCl-] = 0.050 M, then what is the pH of this aqueous solution? (a) (b) (c)arrow_forwardThe active ingredient of bleach such as Clorox is sodium hypochlorite (NaClO). Its conjugate acid, hypochlorous acid (HClO), has a Ka of 3.0 × 10–8. (a) The undiluted bleach contains roughly 1 M NaClO.Calculate the pH of 1 M NaClO solution. (b) Some applications require extremely diluted bleach solution, such as swimming pools. Suppose the solution in (a) is diluted by 10,000-fold. Calculate the pH of the diluted solution, and demonstrate that you can still neglect the autoionization of water in your calculation. (c) Suppose the solution in (a) is diluted by 1 million-fold, briefly explain how your approach willbe different. Write the equation with [H3O+] as the unknown, but you do not need to solve it.arrow_forwardThe active ingredient of bleach such as Clorox is sodium hypochlorite (NaClO). Its conjugate acid, hypochlorous acid (HClO), has a Ka of 3.0 × 10–8. (a)The undiluted bleach contains roughly 1 M NaClO. Calculate the pH of 1 M NaClO solution. (b)Some applications require extremely diluted bleach solution, such as swimming pools. Suppose the solution in (a) is diluted by 10,000 -fold. Calculate the pH of the diluted solution, and demonstrate that you can still neglect the autoionization of water in your calculation. (c)Suppose the solution in (a) is diluted by 1million-fold, briefly explain how your approach will be different. Write the equation with [H3O+] as the unknown, but you do not need to solve it.arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning


