
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781133104261
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 9OQ
A child is practicing for a BMX race. His speed remains constant as he goes counterclockwise around a level track with two straight sections and two nearly semicircular sections as shown in the aerial view of Figure OQ5.9. (a) Rank the magnitudes of his acceleration at the points A, B, C, D, and E from largest to smallest. If his acceleration is the same size at two points, display that fact in your ranking. If his acceleration is zero, display that fact. (b) What are the directions of his velocity at points A, B, and C? For each point, choose one: north, south, east, west, or nonexistent. (c) What are the directions of his acceleration at points A, B, and C?
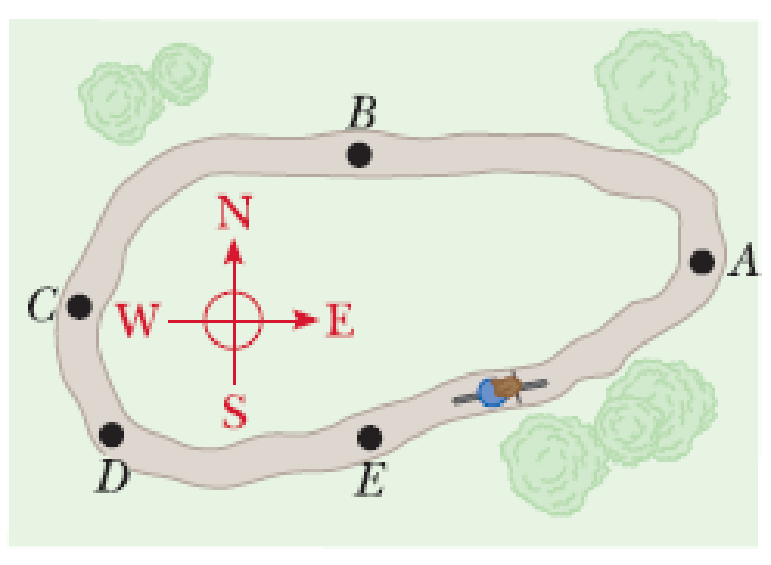
Figure OQ5.9
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A roller coaster at the Six Flags Great America amusement park in Gurnee, Illinois, incorporates some clever design technology and some basic physics. Each vertical loop, instead of being circular, is shaped like a teardrop. The cars ride on the inside of the loop at the top, and the speeds are fast enough to ensure that the cars remain on track. The biggest loop is 40.0m high. Suppose the speed at the top is 14.4m/s and the corresponding centripetal acceleration is 2g. (a) What is the radius of the arc of the teardrop at the top? (b)If the total mass of a car plus the riders is M, what force does the rail exert on the car at the top? (c) Suppose the roller coaster had a circular loop of radius 21.4 m. If the cars have the same speed, 14.4 m.s at the top, what is the centipetal acceleration at the top?
The length of the arc is 250 meters, and the time to turn is 37 seconds. Calculate
the x-component of the acceleration (in m/s2) at point B, where the angle is 69°.
3. A car initially traveling
v eastward turns north by
traveling in a circular
path at uniform speed
as shown in Figure P6.3.
The length of the arc
ABC is 235 m, and the
B)
y
Calculate the average speed in m/s. The numbers:
• Length of the arc: 219 meters
• Time to turn: 49 seconds
35.0°
C
В
car completes the turn
in 36.0 s.
Now calculate the y-component of the average acceleration. The book itself is
6)
unclear whether what's asked for is the average of the vector, the magnitude of
A
the vector average, or the average of the magnitude. But the answer at the back
of the book indicates the vector.
Figure P6.3
• Length of the arc: 227 meters
• Time to turn: 46 seconds
Hi, today I had my engineering mechanics 1 test which I completely screwed up. I was quite confident in the uniform circular motion, but I had this problem in my exam which completely confused me. When I read "upward vertical acceleration" my head just start to spin as I couldn't understand what force could cause an upward acceleration. Could you help me with this problem? I bet it is easier than it looks, but still, I am confused about what is asking me and most importantly about the input it is giving me. I don't have my exam paper with me, but on my body diagram, I knew that on the aeroplane were exerted the Force of Contact Fn1 and the Force m1g in the y opposite direction. On the pilot was acting the Force of Contact with the seat of the aeroplane Fn2 and the m2g in the y opposite direction.
Here is the problem:
During an air show an aircraft comes out of a dive at the bottom of a circular arc at a horizontal speed of 97m/s. In the cockpit the aircraft pilot of mass 58kg…
Chapter 5 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Ch. 5.1 - You press your physics textbook flat against a...Ch. 5.1 - A crate is located in the center of a flatbed...Ch. 5.1 - You are playing with your daughter in the snow....Ch. 5.2 - You are riding on a Ferris wheel (Fig. 5.8) that...Ch. 5.3 - Which of the following is impossible for a car...Ch. 5.3 - A bead slides freely along a curved wire lying on...Ch. 5.4 - Consider a sky surfer falling through air, as in...Ch. 5 - The driver of a speeding empty truck slams on the...Ch. 5 - The manager of a department store is pushing...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m moves with acceleration a down...
Ch. 5 - An office door is given a sharp push and swings...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5OQCh. 5 - A pendulum consists of a small object called a bob...Ch. 5 - A door in a hospital has a pneumatic closer that...Ch. 5 - The driver of a speeding truck slams on the brakes...Ch. 5 - A child is practicing for a BMX race. His speed...Ch. 5 - A large crate of mass m is placed on the flatbed...Ch. 5 - Before takeoff on an airplane, an inquisitive...Ch. 5 - Prob. 12OQCh. 5 - As a raindrop falls through the atmosphere, its...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m is sliding with speed vi at...Ch. 5 - A car is moving forward slowly and is speeding up....Ch. 5 - Prob. 2CQCh. 5 - Prob. 3CQCh. 5 - Prob. 4CQCh. 5 - Prob. 5CQCh. 5 - Prob. 6CQCh. 5 - Prob. 7CQCh. 5 - Prob. 8CQCh. 5 - Prob. 9CQCh. 5 - Prob. 10CQCh. 5 - It has been suggested that rotating cylinders...Ch. 5 - Prob. 12CQCh. 5 - Why does a pilot tend to black out when pulling...Ch. 5 - Prob. 1PCh. 5 - Prob. 2PCh. 5 - Prob. 3PCh. 5 - Prob. 4PCh. 5 - Prob. 5PCh. 5 - The person in Figure P5.6 weighs 170 lb. As seen...Ch. 5 - A 9.00-kg hanging object is connected by a light,...Ch. 5 - Prob. 8PCh. 5 - A 3.00-kg block starts from rest at the top of a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 10PCh. 5 - Prob. 11PCh. 5 - A block of mass 3.00 kg is pushed up against a...Ch. 5 - Two blocks connected by a rope of negligible mass...Ch. 5 - Three objects are connected on a table as shown in...Ch. 5 - Why is the following situation impossible? Your...Ch. 5 - Prob. 16PCh. 5 - A light string can support a stationary hanging...Ch. 5 - Why is the following situation impossible? The...Ch. 5 - A crate of eggs is located in the middle of the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 20PCh. 5 - Prob. 21PCh. 5 - A roller coaster at the Six Flags Great America...Ch. 5 - Prob. 23PCh. 5 - Prob. 24PCh. 5 - Prob. 25PCh. 5 - A pail of water is rotated in a vertical circle of...Ch. 5 - Prob. 27PCh. 5 - A child of mass m swings in a swing supported by...Ch. 5 - Prob. 29PCh. 5 - (a) Estimate the terminal speed of a wooden sphere...Ch. 5 - Prob. 31PCh. 5 - Prob. 32PCh. 5 - Prob. 33PCh. 5 - A 9.00-kg object starting from rest falls through...Ch. 5 - Prob. 35PCh. 5 - Prob. 36PCh. 5 - Prob. 37PCh. 5 - Prob. 38PCh. 5 - Prob. 39PCh. 5 - Prob. 40PCh. 5 - Prob. 41PCh. 5 - Prob. 42PCh. 5 - Consider the three connected objects shown in...Ch. 5 - A car rounds a banked curve as discussed in...Ch. 5 - Prob. 45PCh. 5 - An aluminum block of mass m1 = 2.00 kg and a...Ch. 5 - Figure P5.47 shows a photo of a swing ride at an...Ch. 5 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 5 - A space station, in the form of a wheel 120 m in...Ch. 5 - A 5.00-kg block is placed on top of a 10.0-kg...Ch. 5 - In Example 6.5, we investigated the forces a child...Ch. 5 - Prob. 52PCh. 5 - Prob. 53PCh. 5 - Prob. 54PCh. 5 - Prob. 55PCh. 5 - Prob. 56PCh. 5 - Prob. 57PCh. 5 - Why is the following situation impossible? A book...Ch. 5 - A single bead can slide with negligible friction...Ch. 5 - An amusement park ride consists of a large...Ch. 5 - Prob. 61PCh. 5 - Prob. 62PCh. 5 - Prob. 63PCh. 5 - If a single constant force acts on an object that...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A stunt rider on a motorcycle rides around a large, vertical loop with a radius of 19 m. How fast must he ride to avoid falling at the top of the loop?arrow_forwardYou have put a sonar device at the top of a frictionless inclined plane, as shown in the diagram below. That device allows you to measure the distance an object is from the device, as well as the speed and the acceleration of that object. If we decide that the origin (h = 0) is at the sonar device, we want to know what the height change is as we slide down the incline. 0 For an angle below the horizontal of 6.46, we see that our object has slid a distance 1.13 m, as measured along the incline itself. Calculate the height change in meters - and report your answer as a negative number. (This value would be useful for calculating the change in gravitational potential energy, as we will do in the lab.) h=o 10% O i 26 QUATU 99+ hp X 55 83°F 3:11 PM 10/16/2022 Ctrl 0arrow_forwardYou have put a sonar device at the top of a frictionless inclined plane. That device allows you to measure the distance an object is from the device, as well as the speed and the acceleration of that object. If we decide that the origin (h = 0) is at the sonar device, we want to know what the height change is as we slide down the incline. For an angle below the horizontal of 9.74°, we see that our object has slid a distance 0.54 m, as measured along the incline itself. - Calculate the height change and report your answer as a negative number. (This value would be useful for calculating the change in gravitational potential energy, as we will do in the lab.) h=o earrow_forward
- You are designing the section of a roller coaster ride shown in the figure. Previous sections of the ride give the train a speed of 10.7 m/s at the top of the incline, which is h = 36.3 m above the ground. As any good engineer would, you begin your design with safety in mind. Your local government's safety regulations state that the riders' centripetal acceleration should be no more than n = 1.93 g at the top of the hump and no more than N = 5.77 g at the bottom of the loop. For this initial phase of your design, you decide to ignore the effects of friction and air resistance. (Figure not to scale) Rhump What is the minimum radius Rhump you can use for the semi-circular hump? = What is the minimum radius Roop you can use for the vertical loop? R₁00p R. = hump Roop m marrow_forwardA skier is at the top of a hill with height h. Starting from rest, the skier goes down to a flat area. On this flat area, there is a section of the slope with length D where the snow has melted (there is friction here). After passing the melted section, the skier goes up a smaller hill of height h2. At the top of this hill there is a drop off and the skier launches off of it with a horizontal speed. At what horizontal distance from the base of the jump does the skier land?arrow_forwardYou need to get into your fourth-floor apartment, but you have forgotten your key to the main ground floor door of the building. You call up to your lazy roommate to come down and let you in, but he says he will throw the keys down to you instead. The window that he throws the keys out of is 13 meters above the ground, and he chucks them with a speed of 2m/s at an angle of 20 degrees above horizontal. The acceleration due to gravity near the surface of earth is 9.8 m/s?. How far back from the window do you need to stand to catch the keys?arrow_forward
- You are designing the section of a roller coaster ride shown in the figure. Previous sections of the ride give the train a speed of 11.3 m/s at the top of the incline, which is h = 37.5 m above the ground. As any good engineer would, you begin your design with safety in mind. Your local government's safety regulations state that the riders' centripetal acceleration should be no more than N = 5.37 g at the top of the hump and no more than N = 5.37 g at the bottom of the loop. For this initial phase of your design, you decide to ignore the effects of friction and air resistance. (Figure not to scale)arrow_forwardYou are designing the section of a roller coaster ride shown in the figure. Previous sections of the ride give the train a speed of 10.7 m/s at the top of the incline, which is h=37.5 m above the ground. As any good engineer would, you begin your design with safety in mind. Your local government's safety regulations state that the riders' centripetal acceleration should be no more than n=1.73 g at the top of the hump and no more than N=5.45 gat the bottom of the loop. For this initial phase of your design, you decide to ignore the effects of friction and air resistance. (Figure not to scale)What is the minimum radius Rhump you can use for the semi-circular hump?What is the minimum radius Rloop you can use for the vertical loop?arrow_forwardIn the vertical jump, an Kobe Bryant starts from a crouch and jumps upward to reach as high as possible. Even the best athletes spend little more than 1.00 s in the air (their "hang time"). Treat Kobe as a particle and let ymax be his maximum height above the floor. Note: this isn't the entire story since Kobe can twist and curl up in the air, but then we can no longer treat him as a particle. Hint: Find v0 to reach y_max in terms of g and y_max and recall the velocity at y_max is zero. Then find v1 to reach y_max/2 with the same kinematic equation. The time to reach y_max is obtained from v0=g (t), and the time to reach y_max/2 is given by v1-v0= -g(t1). Now, t1 is the time to reach y_max/2, and the quantity t-t1 is the time to go from y_max/2 to y_max. You want the ratio of (t-t1)/t1 Note from Asker: I am generally confused on how to manipulate the formulas, so if you could show every step that would be great, Thank You. Part A Part complete To explain why…arrow_forward
- You are designing the section of a roller coaster ride shown in the figure. Previous sections of the ride give the train a speed of 10.7 m/s at the top of the incline, which is h = 36.7 m above the ground. As any good engineer would, you begin your design with safety in mind. Your local government's safety regulations state that the riders' centripetal acceleration should be no more than n = 1.85 g at the top of the hump and no more than N = 5.53 g at the bottom of the loop. For this initial phase of your design, you decide to ignore the effects of friction and air resistance. (Figure not to scale) h Roop terms of use contact us help about us privacy policy careersarrow_forwardA prankster flips a coin off of the Empire Building at a height of 1054 feet above the ground. The initial vertical velocity of the coin is 1.20m/s. In real life, air resistance would limit the maximum speed the coin can attain during its fall, but if air resistance were not a factor and assuming it has practically no horizontal motion, answer the following questions. (1 foot = 0.3048m) a. What would the coin's velocity be when it hits the ground? b. How long would it take to hit? c. How high would the coin be halfway through the total falling time, and how fast would it be falling then?arrow_forwardA space shuttle lands on a distant planet where the gravitational acceleration is 2.0 ( We do not know thelocal units of length and time , but they are consistent throughout the problem). The shuttle coasts along aleve, frictionless plane with a speed of 6.0. It then coasts up a frictionless ramp of height 5.0 and angle 0f 30°.After a brief ballistic flight, it lands a distance S from the ramp. Solve for S in local units of length. Assume theshuttle is small compared to the local length unit and that all atmospheric effects are negligible. Use x and y components.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Newton's First Law of Motion: Mass and Inertia; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1XSyyjcEHo0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY