
(a)
Interpretation: An explanation for the differences observed in the
Concept introduction: The glass transition temperature and the melt transition temperature are often used to characterize the behavior of a polymer on heating. They are denoted by
Answer to Problem 30.37P
The given
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of polymers is,
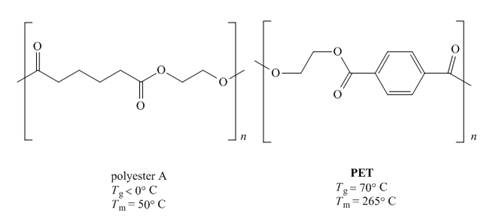
Figure 1
The above polymer chains have both crystalline regions and amorphous regions. The ordered crystalline regions are called crystallites. Crystallites are the sections where polymer chain is bind together by intermolecular interactions. On the contrary amorphous regions are sections where polymer chains are randomly arranged. These sections are held together by weak intermolecular interactions.
A polymer containing high crystallites area possesses high
The given
The given
(b)
Interpretation: An explanation for the differences observed in the
Concept introduction: The glass transition temperature and the melt transition temperature are often used to characterize the behavior of a polymer on heating. They are denoted by
Answer to Problem 30.37P
The given
Explanation of Solution
The given pair of polymers is,
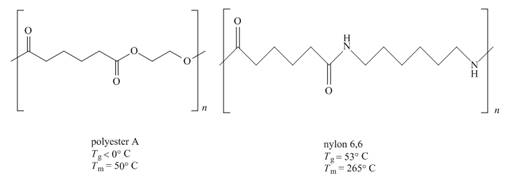
Figure 2
The above polymer chains have both crystalline regions and amorphous regions. The ordered crystalline regions are called crystallites. Crystallites are the sections where polymer chain is bind together by intermolecular interactions. On the contrary amorphous regions are sections where polymer chains are randomly arranged. These sections are held together by weak intermolecular interactions.
A polymer containing high crystallites area possesses high
The given
The given
(c)
Interpretation: The comparison between the
Concept introduction: The glass transition temperature and the melt transition temperature are often used to characterize the behavior of a polymer on heating. They are denoted by
Answer to Problem 30.37P
The
Explanation of Solution
Kevlar is a polyamide, synthesized by
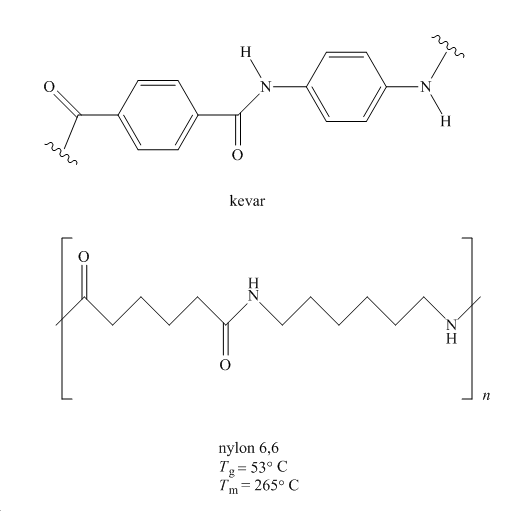
Figure 3
Since more ordered polymers have more
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 30 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Epoxy adhesives are prepared in two steps. SN2 reaction of the disodium salt of bisphenol A with epichlorohydrin forms a prepolymer, which is then cured by treatment with a triamine such as H2NCH2CH2NHCH2CH2NH2. Draw structures to show how addition of the triamine results in a strengthening of the polymer.arrow_forwardp-toluic acid is prepared from 3.42 grams of p-Bromotoluene. When p-Bromotoluene was mixed with dry ether, the mixture was warmed until the ether begins to boil (34.6 °C). When the reaction is almost complete, dry ice (3-4 mL in a beaker) was prepared and the mixture was poured into it. After some time, 5 mL of 6 N HCl was added. The solvent used for the recrystallization is 100 mL of 30% ethanol. The reaction equation is given on the figure. What is the actual yield? What is the theoretical yield? How many moles of p-toluic acid was produced?arrow_forwardAfter looking the chemical structure of nylon (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nylon) what interaction would cause a dye to bind to nylon fabric? dipole-dipole electrostatic hydrogen bonding van der waals/london dispersionarrow_forward
- 3. (a) Draw structures analogous to structure 37 and 38 for the six possible tetrads of poly(methyl methacrylate). (b) How many pentads are possible? Write the mr designations (not structures) of each. H RH R H HH H 37 H RR H H HH H 38arrow_forwardWrite chemical equations of the reactions of ethanoic acid with(a) Sodium(b) Sodium carbonate(c) Ethanol in the presence of conc. H2SO4arrow_forwardExplain the Synthesis of adipic acid and 1,6-diaminohexane for nylon 6,6 synthesis ?arrow_forward
- CH,OCH,CI SnCl, CH,CI The chloromethylated polystyrene resin used for Merrifield solid-phase peptide synthesis is prepared by treatment of polystyrene with chloromethylmethyl ether and a Lewis acid catalyst. The reaction involves the following steps: 1. Reaction of the ether with the Lewis acid to form cation 1; 2. Electrophilic aromatic substitution to form resonance stzbilized cation 2: 3. Deprotonation yields aromatic ether 3: 4. Protonation to žorm protonated ether 4; 5. Displacement by chloride ion to form the final product Write out the mechanism on a separate sheet of paper and then draw the structure of the resonance contributors of the resonance stabilized cation 2. • Use Rl groups to indicate the points where the polymer repeats. The R group tool is located in the charges and lone pairs drop-down menu. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. • Separate resonance structures using the symbol from the…arrow_forwardWhat could be a potential use of adipic acid? A) Not much, adipic acid is a 1,6-dicarboxylic acid, so it easily decarboxylates. B) Adipic acid is extensively used in turophilic chemistry. C) Adipic acid is structurally related to sebacic acid. - We used sabacic acid to make 6,1d-Nylon. So if adipic acid were converted into its acid chloride, and then reacted with hexane-1,6-diamine, one could make 6,6-Nylon. D) Adipic acid is extremely toxic, so it is seldomly used in synthetic chemistry.arrow_forwardAspirin is the common name for the compound acetylsalicylic acid, widely used as a fever reducer and as a pain killer. Salicylic acid, whose name comes from Salix, the willow family of plants, was derived from willow bark extracts. In folk medicine, willow bark teas were used as headache remedies and other tonics. Nowadays, salicylic acid is administered in the form of aspirin which is less irritating to the stomach than salicylic acid. To prepare aspirin, salicylic acid is reacted with an excess of acetic anhydride. A small amount of a strong acid is used as a catalyst which speeds up the reaction. In this experiment, phosphoric acid will be used as the catalyst. The excess acetic acid will be quenched with the addition of water. The aspirin product is not very soluble in water so the aspirin product will precipitate when water is added. The synthesis reaction of aspirin is shown below: Actic anhydride 5 ml. Acetic acid Salicylic acid 28 Acetylsalicylie acid Procedure 1) Mix salicylic…arrow_forward
- A mixture of compounds is dissolved in ether, and extracted with 10% NaHCO3 solution. The aqueous extract is treated with 6M HCI solution, and extracted with dichloromethane. If the mixture contains an amine, where is it? The bottom layer of the first extraction O The top layer of the second extraction The top layer of the first extraction The bottom layer of the second extractionarrow_forwardThere are several isomeric alcohols and ethers of molecular formula C5H12O. Propose a structure for the isomer. Isomer B: δ = 0.92 (t, 7.8 Hz, 3 H), 1.20 (s, 6H), 1.49 (q, 7.8 Hz, 2H), 1.85 (s, 1H) ppmarrow_forward5 The compounds labeled benzophenone-3 (CH,O,) and benzophenone-5 (CHNAO,S) are found in certain sunscreens. Would you expect a sunscreen made with benzophenone-3 or benzophenone-5 to be more waterproof? Explain your choice.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole





