
Concept explainers
Sections 11.2–11.4
11.1 (The Triangle class) Design a class named Triangle that extends GeometricObject. The class contains:
■ Three double data fields named side1, side2, and side3 with default values 1.0 to denote three sides of a triangle.
■ A no-arg constructor that creates a default triangle.
■ A constructor that creates a triangle with the specified side1, side2, and side3.
■ The accessor methods for all three data fields.
■ A method named getArea() that returns the area of this triangle.
■ A method named getPerimeter() that returns the perimeter of this triangle.
■ A method named toString() that returns a string description for the triangle.
For the formula to compute the area of a triangle, see
return "Triangle: side1 = " + side1 + " side2 = " + side2 + " side3 = " + side3;
Draw the UML diagrams for the classes Triangle and GeometricObject and implement the classes. Write a test program that prompts the user to enter three sides of the triangle, a color, and a Boolean value to indicate whether the triangle is filled. The program should create a Triangle object with these sides and set the color and filled properties using the input. The program should display the area, perimeter, color, and true or false to indicate whether it is filled or not.
Program Plan:
- Include the required import statement.
- Define the main class.
- Define the main method using public static main.
- Declare the input scanner.
- Get the three sides of the triangle from the user.
- Create an object for the “Triangle” class.
- Get the color from the user and call the “setColor” method with the parameter “color”.
- Get the Boolean value for filled the triangle and call the “setFilled” method with the parameter “filled”.
- Display the output.
- Define the main method using public static main.
- Define the “GeometricObject” class.
- Declare the required variables.
- Define the default constructor and constructor for the class.
- Define the accessor and matator.
- The “isFilled” and “setColor” method will return the value to the main class.
- Define the derived class “Triangle” from the “GeometricObject” class.
- Declare the required variables.
- Define the default constructor and constructor for the class.
- Define the accessor.
- The “getArea()” method will calculate the area of triangle and then return the result.
- The “getPerimeter()” method will return the perimeter of the triangle.
- The “toString()” method will return the three sides of the triangle.
The below program is used to display the area, perimeter and sides of the triangle as follows:
Explanation of Solution
Program:
//import statement
import java.util.Scanner;
//class Excersise11_01
public class Exercise11_01
{
// main method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// declare the scanner variable
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
//get the input from the user
System.out.print("Enter three sides: ");
//declare the variables
double side1 = input.nextDouble();
double side2 = input.nextDouble();
double side3 = input.nextDouble();
//create an object for the "Triangle" class
Triangle triangle = new Triangle(side1, side2, side3);
//get the input from the user
System.out.print("Enter the color: ");
String color = input.next();
//call the "setColor" function
triangle.setColor(color);
//get the input from the user
System.out.print("Enter a boolean value for filled: ");
boolean filled = input.nextBoolean();
//call the "setFilled" function
triangle.setFilled(filled);
//print the output
System.out.println("The area is " + triangle.getArea());
System.out.println("The perimeter is "
+ triangle.getPerimeter());
System.out.println(triangle);
}
}
//definition of class "GeometricObject"
class GeometricObject
{
/* declare the required variables and initialize it */
private String color = "white";
private boolean filled;
private java.util.Date dateCreated;
//definition of default constructor
public GeometricObject()
{
//create an object
dateCreated = new java.util.Date();
}
//definition of constructor
public GeometricObject(String color, boolean filled)
{
//create an object
dateCreated = new java.util.Date();
//set the value
this.color = color;
this.filled = filled;
}
//definition of accessor
public String getColor()
{
//return the color
return color;
}
//definition of mutator
public void setColor (String color)
{
//set the color
this.color = color;
}
//definition of the "isFilled" method
public boolean isFilled()
{
//return the value
return filled;
}
//definition of the "setFilled" method
public void setFilled(boolean filled)
{
//set the value
this.filled = filled;
}
//definition of the "getDateCreated" method
public java.util.Date getDateCreated()
{
//return the value
return dateCreated;
}
//definition of the "toString" method
public String toString()
{
//return the value
return "created on " + dateCreated + "\ncolor: " + color + " and filled: " + filled;
}
}
//definition of derived class "Triangle"
class Triangle extends GeometricObject
{
/* declare the required variables and initialize it */
private double side1 = 1.0, side2 = 1.0, side3 = 1.0;
/*definition of Constructor */
public Triangle()
{
}
/* definition of Constructor */
public Triangle(double side1, double side2, double side3)
{
this.side1 = side1;
this.side2 = side2;
this.side3 = side3;
}
//definition of accessor
public double getSide1()
{
//return the value
return side1;
}
//definition of accessor
public double getSide2()
{
//return the value
return side2;
}
//definition of accessor
public double getSide3()
{
//return the value
return side3;
}
/*override method of "getArea" in GeometricObject */
public double getArea()
{
//declare and calculate the value
double s = (side1 + side2 + side3) / 2;
//return the value
return Math.sqrt(s * (s - side1) * (s - side2) * (s - side3));
}
/*override method of "getPerimeter" in GeometricObject */
public double getPerimeter()
{
//return the value
return side1 + side2 + side3;
}
//definition of "toString" method
public String toString()
{
// return the three sides
return "Triangle: side1 = " + side1 + " side2 = " + side2 +" side3 = " + side3;
}
}
UML diagram:
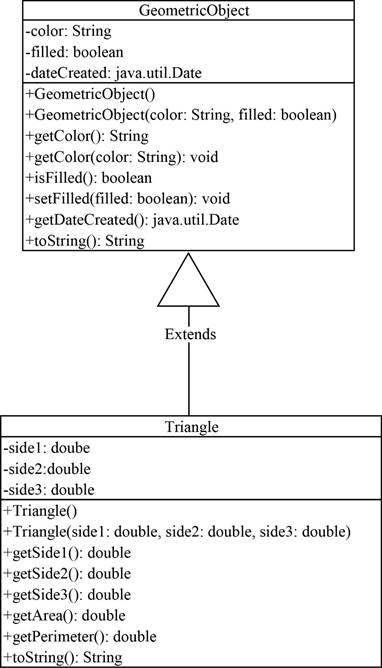
Explanation:
The above UML diagram the “GeometricObject” is a parent class which contains “color”, “filled”, “dateCreated” variables and “GeometricObject()”, “GeometricObject(String color, boolean filled)”, “getColor()”, “getColor(String color)”, “isFilled()”, “setFilled(boolean filled)”, “getDateCreated()” and “toString()” methods.
The “Triangle” is the child class extended from “GeometricObject” class it contains “side1”, “side2” and “side3” variables and “Triangle()”, “Triangle(double side1, double side2, double side3)”, “getSide1()”, “getSide2()”, “getSide3()”, “getArea()”, “getPerimeter()” and “toString()” methods.
Enter three sides: 2
3
4
Enter the color: black
Enter a boolean value for filled: true
The area is 2.9047375096555625
The perimeter is 9.0
Triangle: side1 = 2.0 side2 = 3.0 side3 = 4.0
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Introduction to Java Programming and Data Structures, Comprehensive Version (11th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (3rd Edition)
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Concepts of Programming Languages (11th Edition)
Starting out with Visual C# (4th Edition)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- Exercise: Exercises Write a class named Octagon that extends GeometricObject and implements the Comparable and Cloneable interfaces. Assume all eight sides of the octagon are of equal length. The area can be computed using the following formula: The Octagon class has a private double data field named side with its getter and setter methods. The class has a no-arg constructor that creates an Octagon with side 0, and a constructor to create an Octagon with a specified side. Write a test program that creates an Octagon object with side value 5 and displays its area and perimeter. Create a new object using the clone method, and compare the two objects using the compareTo method. As far as classes go, the abstract GeometricObject class contains the abstract doubles getArea() and getPerimeter(). The programming language used in this exercise is Java, and it covers the Interfaces topic. I did get how most of the program should look like, but I'm facing trouble understanding a few…arrow_forwardClass: Square Create a class called "Square", which is inherited from“TwoDimensionShape” class. The "Square" class is used to calculate theArea and the Perimeter of square shapes when their side-length is given, or in contrast,finding the side-length of the square when the Area or the Perimeter of the square is given.The specifications of this class are below. Data Members (Attributes): All are private. sideLength: the sidelight (L) of the square. Methods/Operations/Getters/Setters: Default Constructor: when creating an object this constructor must set the side-length of the square by calling the method setSideLength(). Also, this constructor willcall the findArea() and the findPerimeter() in addition to summaryPrint() to calculateand print all needed information. User-Defined Constructor: when creating an object this constructor shouldfind the side-length of the square by calling the method findSquareSideLength()and pass the Area or the…arrow_forward-------Answer code question below--------- Create a class Student with the following characteristics Implements Cloneable interface. Contain two member variables RollNo & Name. Initialize member variable of using the parameterized (2 parameters) constructor. Implement getRollNo and getName methods which returns respective variable values. Input: PGMCA2017 Amit where, The first line contains RollNo. The second line contains Name. Output: PGMCA2017 Amit solution.java code below: *Do not change any other part of the code other than where it says you can.arrow_forward
- Create a class Car, which contains • Three data members i.e. carName (of string type), ignition (of bool type), and currentSpeed (of integer type)• A no-argument constructor to initialize all data members with default values• A parameterized constructor to initialize all data members with user-defined values• Three setter functions to set values for all data members individually• Three getter function to get value of all data members individually• A member function setSpeed( ) // takes integer argument for setting speedDerive a class named Convertible that contains• A data member top (of Boolean type)• A no-argument constructor to assign default value as “false” to top• A four argument constructor to assign values to all data-members i.e. carName, ignition,currentSpeed and top.• A setter to set the top data member up• A function named show() that displays all data member values of invoking objectWrite a main() function that instantiates objects of Convertible class and test the…arrow_forwardCreate a class Car, which contains • Three data members i.e. carName (of string type), ignition (of bool type), and currentSpeed (of integer type) • A no-argument constructor to initialize all data members with default values • A parameterized constructor to initialize all data members with user-defined values• Three setter functions to set values for all data members individually• Three getter function to get value of all data members individually• A member function setSpeed( ) // takes integer argument for setting speedDerive a class named Convertible that contains • A data member top (of Boolean type) • A no-argument constructor to assign default value as “false” to top• A four argument constructor to assign values to all data-members i.e. carName, ignition, currentSpeed and top.• A setter to set the top data member up • A function named show() that displays all data member values of invoking objectWrite a main() function that instantiates objects of Convertible class and test the…arrow_forward-------Answer code question below--------- Create a class Student with the following characteristics Implements Cloneable interface. Contain two member variables RollNo & Name. Initialize member variable of using the parameterized (2 parameters) constructor. Implement getRollNo and getName methods which returns respective variable values. Input: PGMCA2017 Amit where, The first line contains RollNo. The second line contains Name. Output PGMCA2017 Amit solution.java code below:arrow_forward
- Colorful bubbles In this problem, you will use the Bubble class to make images of colorful bubbles. You will use your knowledge of classes and objects to make an instance of the Bubble class (aka instantiate a Bubble), set its member variables, and use its member functions to draw a Bubble into an image. Every Bubble object has the following member variables: X coordinate Y coordinate Size (i.e. its radius) Color Complete main.cc Your task is to complete main.cc to build and draw Bubble objects based on user input. main.cc already does the work to draw the Bubble as an image saved in bubble.bmp. You should follow these steps: First, you will need to create a Bubble object from the Bubble class. Next, you must prompt the user to provide the following: an int for the X coordinate, an int for the Y coordinate, an int for the Bubble's size, and a std::string for the Bubble's color. Next, you must use the user's input to set the new Bubble object's x and y coordinates, the size, and the…arrow_forwardAnimal: Create a class Animal and Add a protected data member named id of integer type. • Add get/set methods for id data member in Animal class with public access. Also provide default constructor this should initialize id to 0. • Also provide parameterized constructor and toString method. • Add an abstract method tellAboutSelf method to Animal class with public access • Add another abstract method speak method to Animal class. Reptile, Bird, Mammal Next create the three child classes which extends form Animal class. • Add a default constructor to each of the above created class. The constructor should initialize the id data member id, Reptile, Bird and Mammal, to 1, 2 and 3 respectively also it display a message “(class Name)’s default constructor”. E.g. for Bird it says “Bird’s default constructor”. • Add a parameterized constructor to each of the above created class. The constructor should initialize the id data member, Reptile, Bird and Mammal, to the specified id passed to the…arrow_forwardJAVA 2 LANGUAGE 8.2 (The Stock class) Following the example of the Circle class in Section 8.2, design a class named Stock that contains: ■ A string data field named symbol for the stock’s symbol. ■ A string data field named name for the stock’s name. ■ A double data field named previousClosingPrice that stores the stock price for the previous day. ■ A double data field named currentPrice that stores the stock price for the current time. ■ A constructor that creates a stock with the specified symbol, name, previousClosingPrice, and currentPrice. ■ A method named getChangePercent() that returns the percentage changed from previousClosingPrice to currentPrice. The formula to be used is (currentPrice - previousClosingPrice) / previousClosingPrice. Draw the UML diagram for the class and then implement the class (write the code for the class). Write a test program (application) in which you create a Stock object stock1 with the stock symbol ORCL, the name Oracle Corporation, the…arrow_forward
- Calculator Class In the file Calculator.java, write a class called Calculator that emulates basic functions of a calculator: add, subtract, multiply, divide, and clear. The class has one private member field called value for the calculator's current value. Implement the following Constructor and instance methods as listed below: public Calculator() - Constructor method to set the member field to 0.0 public void add(double val) - add the parameter to the member field public void subtract(double val) - subtract the parameter from the member field public void multiply(double val) - multiply the member field by the parameter public void divide(double val) - divide the member field by the parameter public void clear( ) - set the member field to 0.0 public double getValue( ) - return the member field Given two double input values num1 and num2, the program outputs the following values: The initial value of the instance field, value The value after adding num1 The value after…arrow_forwardTask 2: abstract Class: TwoDimensionShape Create an abstract class called "TwoDimensionShape", which implements interface "Shape". See below the abstract class "TwoDimensionShape" specifications: > Data Members (Attributes): All data members are privet. o uName: User name. o sName: Geometric Shape name. > Methods: o findArea(): abstract method, no implementation, it should return the area of 2D shape. o findPerimeter(): abstract method, no implementation, it should return the Perimeter of 2D shape. a proper coding: • Standard naming convention (class name, attribute, and method). Completed program compiles and runs. • Attributes given along with their visibility and type Methods given along with visibility, return type and parameters.arrow_forwardDesign a class named StopWatch. The class contains:■■ Private data fields startTime and endTime with getter methods.■■ A no-arg constructor that initializes startTime with the current time.■■ A method named start() that resets the startTime to the current time.■■ A method named stop() that sets the endTime to the current time.■■ A method named getElapsedTime() that returns the elapsed time for thestopwatch in milliseconds.Draw the UML diagram for the class then implement the class. Write a test programthat measures the execution time of sorting 100,000 numbers using selection sort.arrow_forward
 EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,

