
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 9.4, Problem 1bT
Three light waves are represented at right. The diagram are drawn to the same scale.
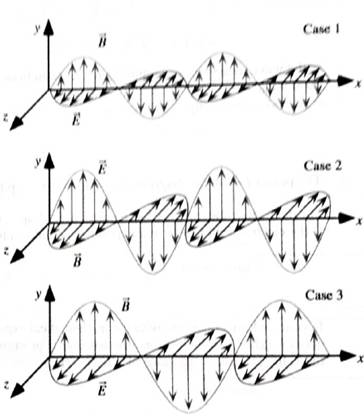
1. How is the wave in case 1 different from the wave in case2? Explain how you can tell from the diagrams.
2. If the wave in case 2 were green light, could the wave in case 3 be red, light or blue light? Explain.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule02:32
Students have asked these similar questions
All answers require full explanations in complete sentences.
The figure below shows a spherical bubble of CO2 gas in a liquid. The index of refraction of the
liquid is 1.5 times larger than that of the gas. A light ray in the liquid is incident on the bubble as
shown. The black dot identifies the center of the bubble.
Draw, precisely, a reasonable ray transmitted into the bubble and explain how you
why it looks as you have drawn it.
determined
Solve the following problems completely. Draw and label appropriate diagrams.
1. A light ray in the air is incident on an air to glass boundary at an angle of 45.0o and is refracted inthe glass of 30.0o with the normal. What is the index of refraction of the glass?
In the figure at right the light is crossing a vertical interface with the normal
Medium n1
marked as a dashed line. The light is coming from the left and crossing to
the right..
Medium n2
normal
Which is larger?
The index of refraction is larger
The speed of light is faster in
Choose the equation or equations that you will need to use to calculate n2 given the angles of incidence and
refraction and then to find the speed of light in medium n2.
Select one or more:
a. Force on an object mass m moving in a circle of radius R: F = mv2/R
b. B-field of a long straight wire: B = Hol/2nR
c. Snell's law: n;sin0, = n2sin02
d. Doppler shift: f' = f(1 ± u/c)
e. C =
= fA
f. Magnetic Force on a moving charge: F = qvBsin0
g. Force on a current carrying wire: F = BILsine
h. Mirror or Thin Lens Equation: 1/d, + 1/d; =1/f, h/h¡ = -d/d;
Chapter 9 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 9.1 - A piece of yarn has been attached to the spring....Ch. 9.1 - During the demonstration, did any of the following...Ch. 9.1 - During the demonstration, each of the following...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 2aTCh. 9.1 - Prob. 2bTCh. 9.1 - Prob. 3aTCh. 9.1 - Prob. 3bTCh. 9.2 - Describe what happens after the pulse reaches the...Ch. 9.2 - Compare the speed of a pulse in one spring to the...Ch. 9.2 - In answering the questions below, assume that each...
Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 2aTCh. 9.2 - Prob. 2bTCh. 9.2 - Prob. 3aTCh. 9.2 - Prob. 4aTCh. 9.2 - Which of the following quantities are different on...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 4cTCh. 9.3 - Prob. 1aTCh. 9.3 - Prob. 1bTCh. 9.3 - Prob. 1cTCh. 9.3 - Prob. 1dTCh. 9.3 - Prob. 1eTCh. 9.3 - Prob. 2aTCh. 9.3 - Prob. 2bTCh. 9.3 - Prob. 2cTCh. 9.3 - Prob. 2dTCh. 9.3 - Each of the diagrams at right shows a ray incident...Ch. 9.3 - Does the ray representing a wave always “bend”...Ch. 9.4 - Shown below are mathematical and pictorial...Ch. 9.4 - Three light waves are represented at right. The...Ch. 9.4 - Write an expression for the force exerted on a...Ch. 9.4 - Imagine that the electromagnetic wave in section I...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 3aTCh. 9.4 - Suppose that the electric field in a light wave...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
A satellite can orbit at 5km above the Moon but not at 5km above the Earth. Why?
Conceptual Integrated Science
Using the definitions in Eqs. 1.1 and 1.4, and appropriate diagrams, show that the dot product and cross produc...
Introduction to Electrodynamics
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
5. At one point in space, the electric potential energy of a 15 nC charge is 45 ?J.
a. What is the electric pot...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Q16.12 A small fraction of the energy in a sound wave is absorbed by the air through which the sound passes. Ho...
University Physics (14th Edition)
The local historical society has asked your assistance in writing the interpretive material for a display featu...
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Look for the different indices of refraction and answer the following below. 1. A classic observation of refraction occurs when a pencil is placed in a glass half filled with water. Do this and observe the shape of the pencil when you look at the pencil sideways, that is, through air, glass, water. Explain your observations. Draw ray diagrams for the situation.arrow_forwardA ray is incident upon a reflective surface at an angle of 0;=64.4° relative to the direction normal to the surface (see image below to help visualize the situation). What is the angle of the reflected ray (0) relative to the normal direction (in degrees)? Incident ray 0₁ = 0₁ Normal to surface I 0₁ 0₁ Reflected ray Note: It is understood that the unit of your answer is in degrees, however do not explicitly include units in your answer. Enter only a number. If you do enter a unit, your answer will be counted wrong.arrow_forwardTwo flat mirrors make an angle of 90.0° with each other, as diagrammed below. An incoming ray makes an angle of ? = 45° with the normal of mirror A. Use the law of reflection to determine the angle of reflection from mirror B. ° from the normal line of mirror B. What is unusual about the incoming light for this arrangement of mirrors? The ray reflected from the second mirror is never parallel to the incoming ray.The ray reflected from the second mirror is always parallel to the incoming ray. There is no reflected ray.arrow_forward
- Cal Culator is preforming experiments to determine the index of refraction of two unknown materials. Cal determines that the light follows the paths as shown on the diagrams below. Use this path, a protractor, a calculator, qnd Snell's law to determine the index of refraction of the unknown material. Show all your work in the space beside the diagram.arrow_forwardRefer to the photo below. a. What happened to the white light when it reflected out in the air? Why the light reflected out in such manner when it is white?b. How did the white light reflect out that way?c. What do you call this kind of phenomenon?arrow_forwardOne well-known image of a prism is the following picture a. Given the pattern of light on the far side of the prism, is the index of refraction inside the prism higher or lower than the index of refraction outside the prism? b. List at least one thing that is wrong with this diagram given what we expect the dependence of n on the wavelength of light to be (and assuming the prism is made of a uniform material). c. List at least one thing that is right with this diagram given what we expect the dependence of n on the wavelength of light to be (and assuming the prism is made of a uniform material).arrow_forward
- A ray is incident upon a reflective surface at an angle of 0;=16.3° relative to the direction normal to the surface (see image below to help visualize the situation). What is the angle of the reflected ray (r) relative to the normal direction (in degrees)? Incident ray 0₁ = 0₁ Normal to surface 0₁ Or Reflected ray Note: It is understood that the unit of your answer is in degrees, however do not explicitly include units in your answer. Enter only a number. If you do enter a unit, your answer will be counted wrong.arrow_forwardPlease compute the case problem a, b, and c:A 1,000 lumen source is 4 meter away from the center of a screen.The edge of the screen is 5 meters from the light source.a. What is the intensity of the light falling on the center of the screen?b. What is the intensity of light falling on the edge of the screen?Formula:E = I/d^2 Where : E = is the intensity of the light on the object,lux (lx) or foot candleI = is the intensity of the light at the source,lumen (lm)d = is the distance of the light source from the object,meters or ft. Example Problem1. If the magazine is 2m from the 100 lumen source, what is the intensity of the light failing on themagazine?E = I/d2E = 100/22E = 25 luxarrow_forwardAnswer all questions in the space provided. Box only and all of your answers. Keep all work as organized as possible for the mental health of your grader! V sound = 343 m/s, Vlight = 3 × 10® m/s. W o = 5.67 × 10-8 nglass = 1.5, Nwater = 1.33, m2 K Question 1 Light is incident on the surface of a pond at an angle of 30° with respect to the normal. What is the angle of refraction as the light passes inside the water? Question 2 Calculate the critical angle of glass Question 3 A wave is described by the function: y = 20 sin (1207t – 3.r) (a) What is the maximum amplitude of this wave? (b) What is the linear frequency of this wave? (c) What is the wavelength of this wave? (d) What is the velocity of this wave?arrow_forward
- Part A The diagram below shows the situation described in the problem. The focal length of the lens is labeled f; the scale on the optical axis is in centimeters.Draw the three special rays Ray1, Ray2, and Ray3 as described in the Tactics Box above, and label each ray accordingly. Draw the rays from the tip of the object to the lens. Do not draw the refracted rays. Draw the vectors starting from the tip of the object. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. The length of the vectors will not be graded. +, Vectors: Ray3 Ray through center of lens Ray2 Ray toward far focal point Rayl Ray parallel to axis Unlabeled vector Object 1arrow_forwardPlease continue and explain all symbols. How are related the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection in the reflection of light off a flat, smooth surface? Light that passes into a transparent medium is bent at the boundary and is said to be refracted. What is the angle of refraction?arrow_forwardWhat are the factors that affect how light is observed by the human eye? 2. Give other examples of dispersion, scattering, diffraction, and interference that can be observed in everyday lifearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Domestic Electric Circuits; Author: PrepOnGo Class 10 & 12;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2ZvWaloQ3nk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY