
Concept explainers
(a)
Show that in case of heavy damping
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Since
The expression for the differential equation of over damping as follows:
Differentiate the above equation with respect to ‘t’.
Since the body is released with no initial velocity.
Substitute 0 for t,
Substitute 0 for t,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Apply boundary condition.
For
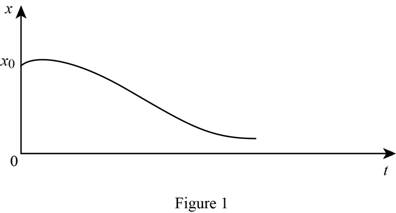
As
Thus the positive answer for the ‘t’ greater than 0 for the equation (4) cannot exist because the exponential (e) is increased to positive power be less than one which is not possible. Hence, the value of x is not becomes zero.
Show the graph of x versus t for the above solution as Figure (1).
(b)
Show that in case of heavy damping
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Since the body is started from O with arbitrary initial velocity.
Substitute 0 for t, 0 for x and
Substitute 0 for t, 0 for x, and
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Apply boundary condition.
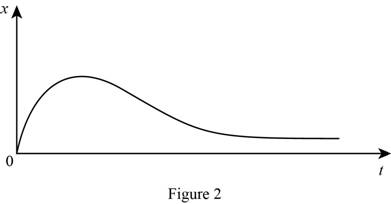
For
For
Show the graph of x versus t for the above solution as Figure (2).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- A spring with a 8-kg mass and a damping constant 2 can be held stretched 0.5 meters beyond its natural length by a force of 1.5 newtons. Suppose the spring is stretched 1 meters beyond its natural length and then released with zero velocity. In the notation of the text, what is the value c2 – 4mk? m'kg/sec? help (numbers) Find the position of the mass, in meters, after t seconds. Your answer should be a function of the variable t with the general form cieat cos(Bt) + cze"s t sin(&t) help (numbers) a = B = * help (numbers) * help (numbers) 8 = * help (numbers) C1 = help (numbers) C2 = 2 help (numbers) kies help us deliver our services. By using our services, you agree to our use of cookies. OK Learn more CONNECT OFF/ON CAPS Charge Po- 14 F4 F5 1- 1+ F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 7 8 R T Y U 5arrow_forwardQUESTION 2 A vibrating system can be modeled with a mass weighs 20 kg and supported on springs and dashpots. The total stiffness of the springs is 2000 N/m and the damping constant is 10 N/m/s. The system is initially at rest and a velocity of 10 m/s is imparted on the mass. Determine the displacement after 1 s.arrow_forward4.11. A damped single degree of freedom mass-spring system is excited at resonance by a harmonic forcing function which has an amplitude of 40 N. The system has mass m of 3 kg, a stiffness coefficient k of 2700 N/m, and a damping coefficient c of 20 N · s/m. If the initial conditions are such that xo = 5 cm, and to = 0, determine the displacement, velocity, and acceleration of the mass after t = 0.2 s.arrow_forward
- Assume that we disturb an undamped system from equilibrium. Sketch and explain a system's time response.arrow_forwardA vibrating system with a mass of 12 kg and a sprinf with a stiffness of 120 N/m. The mass is started in motion from equilibrium position with an initial velocity of 2 m/s in the upward direction and with an applied external force F(t) = 7sint. While in motion the mass is subjected to damping with damping constant of 72 kg/s. - Find the position of the mass (natural response) after 3s. - Find the velocity of the mass (natural response) after 3s. - Find the position of the mass (forced response) after 3s. - Find the velocity of the mass (forced response) after 3s. - Find the position of the mass (complete response) after 2s.arrow_forward(c) The spring-damper-mass system shown in Figure Q3(c) is at rest when strict by a hammer with an initial velocity of 0.4 m/s causing the mass to move upwards. Given that the mass m = 2 kg, spring constant k = 128 N/m and coefficient of viscous damping c = 0.6 Ns/m. (i) Determine the damped frequency of the spring-damper-mass system.arrow_forward
- For a mass-spring oscillator, Newton's second law implies that the position y(t) of the mass is governed by the second-order differential equation my''(t) +by' (t) + ky(t) = 0. (a) Find the equation of motion for the vibrating spring with damping if m= 20 kg, b = 80 kg/sec, k = 260 kg/sec², y(0) = 0.3 m, and y'(0) = -0.3 m/sec. (b) After how many seconds will the mass in part (a) first cross the equilibrium point? (c) Find the frequency of oscillation for the spring system of part (a). (d) The corresponding undamped system has a frequency of oscillation of approximately 0.574 cycles per second. What effect does the damping have on the frequency of oscillation? What other effects does it have on the solution? (a) y(t) = plz answer a-darrow_forward19. A weight of 25 N is suspended from a spring that has a stiffness of 1,000 N/m. The weight vibrates in the vertical direction under a constant damping force. When the weight is initially pulled downward a distance of 10 cm from its static equilibrium position and released, it comes to rest after exactly two complete cycles. Find the magnitude of the damping force.arrow_forward4) Figure below shows a spring-mass- damper system. The mass is subjected to a steady force of P 2 N. The spring constant k 200 N/m, the mass m 5.2 kg and the damping ratio is f= 12.2 N. sec/m. What is the position of the mass after a sufficiently long time of force application? You may assume that the mass is initially at rest, and the spring at time t = 0 is in its unstretched condition. m karrow_forward
- Mohammed Mahad Tabook A lathe can be modeled as an electric motor mounted on a steel table. The table plus rotor have a mass of 100 kg. The rotating parts of the lathe have a mass of 10 kg at a distance 0.1 m from the center. The damping ratio of the system is measured to be zeta= 0.06 (viscous damping) and its natural frequency is 7.5 Hz and the driving frequency is 30HZ The natural frequency in rad/s is Choose.. The driving frequency in rad/s is Choose... The frequency ratio is Choose... The amplitude of the steady-state displacement of the motor (in mm) Choose... the phase shift of the steady state displacement (in rad) is Choose... +arrow_forward1. An object having a mass of 1 gram is attached to the lower end of a spring having a modulus of 29 dynes per centimeter. The mass in turn is adhered to a dashpot that imposes a damping force of 10v dynes, where v(t) is the velocity of the mass at timet in centimeters per second. Determine the motion of the mass if it is pulled down 3 centimeters from equilibrium and then struck upward with a blow sufficient to impart a velocity of 1 centimeter per second. Solve the problem when the initial velocity is (in turn) 2, 4, 7, and 12 centimeters per second.arrow_forwardA vibrating system with a mass of 12 kg and a sprinf with a stiffness of 120 N/m. The mass is started in motion from equilibrium position with an initial velocity of 2 m/s in the upward direction and with an applied external force F(t) = 7sint. While in motion the mass is subjected to damping with damping constant of 72 kg/s. 1. Find the position of the mass (natural response) at any given time. 2. Find the position of the mass (forcedresponse) at any given time. 3. Find the position of the mass (complete response) at any given time. 4. Find the position of the mass (natural response) after 3s. 5. Find the velocity of the mass (natural response) after 3s. 6. Find the position of the mass (forced response) after 3s. 7. Find the velocity of the mass (forced response) after 3s. 8. Find the position of the mass (complete response) after 2s.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





