
Concept explainers
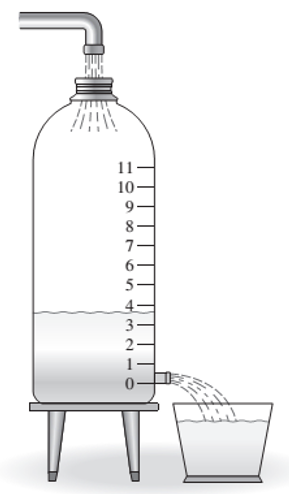
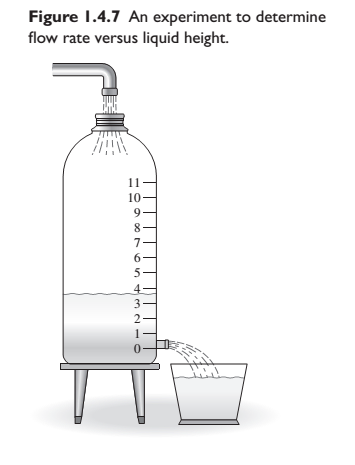
Consider the milk container of Example 1.4.2 (Figure 1.4.7). A straw 9.5 cm long was inserted in the side of the container. While adjusting the tap flow to keep the water height Constant, the time for the outflow to fill a 250-ml cup was measured. This was repeated for several heights. The data are given in the following table.
Obtain a functional description of the volume outflow rate f through the straw as a function of water height h above the hole.

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
System Dynamics
- PROPAGATION OF ERROR You are tasked to supervise the design of 0.5MW wind turbine to be constructed in a Wind Farm in Pililla, Rizal. Suppose the design criteria are as follows: The air density as surveyed after 2 year period averaged at 1.225 kg / cubic meter. The sweeping diameter of the rotor blades is 125m, and the anemometer reading in the area amounts to 4.2m/s on a 2 year period of survey. What is the theoretical power output of the turbine assuming 100% efficiency of operation? Your answer must be in kW and in two decimal places with correct signs. In the previous problem, if the diameter measurement is off by 0.1m and the anemometer reading is also fluctuating by 0.05m/s and if the error measurement for theoretical power output must be limited to 3%, WHY OR WHY NOT should you accept the design? * Show complete solution in paper.arrow_forwardFor a venturi meter given below, the volumetric flow rate is defined in terms of the geometrical parameters, the density of working fluid (p), and density of the manometer liquid (pm) as 4. Q = f(D, D2, A2, g, h, Pmv Pr) %3D Write down the balance equations and show your work to end up with an expression for the volumetric flow rate in terms of the variables defined above.arrow_forward3G 9:.. %79 Final 1st attem... F2 У - ахis Fs F4 F1 х - ахis X- axis y - axis F3 F2 F1 Figure (1) Figure (2) 250 N 36.87 D F2 60° 0.5 m 1 m o! 0.2 m 1 m 300 NE F1 1 m Figure (3) Figure (4) Q1] Answer the following questions: For figure (1): The object is subjected to two forces F1 = 25 N, and F2 = 50 N. Set x = 30°, 0 = 45° , and ß = 30°. 1- What is the magnitude of the resultant of these two forces? a) 39.4 N b) 80.1N c) 41.6 N d) 69.8 N e) 71.4 N f) 46.1 N g) None of them 2 - What is the direction of the resultant force measured counterclockwise from the positive x-axis? а) 14.30 b) 392.6° c) 9.2° d) 322.9° e) 6.8° f) 344.2° g) None of them For figure (2): The arm in is subjected to five forces as follows: F1 = 135 N, F2 = 98 N, F3 = 210 N, F4 = 56 N. If the y – direction resultant force is 144 N, and x = 40°, 0 = 50°, B = 70°: 3 – What is the magnitude of the force F5? a) 318.4 N b) 99.1N c) 151.6 N d) 36.5 N e) 111.2 N f) 18.8 N g) None of them 4 - What is the magnitude of the…arrow_forward
- A physics lab Consist of a large bowl attached to wire. Students hold onto one of the wire the whirl the ball around in circles and count the number of rotations per second. One group finds these numbers: ball mass=320g, wire length=1.3m, number of rotations/second=2.5. The wire is made of steel with a diameter of 1mm and a Young’s modulus of 20x10^10 N/m^2. How much does the wire stretch due to the tension on it? Should the students correct their data for the wire stretching?arrow_forward56.0 mL of two different liquids are poured through a funnel with a narrow exit tube, and the time for all of the liquid to flow through is recorded. Here are some results: time to flow through funnel trial Liquid X Liquid Y 1.60 s 3.62 s 1.52 s 3.44 s 1.44 s 3.56 s Note: the two liquids have the same density. Which statement below is true about these liquids based only on the data in the table? O The intermolecular forces in liquid X are stronger than those in liquid Y. The boiling point of liquid X is higher than the boiling point of liquid Y. The viscosity of liquid X is greater than the viscosity of liquid Y. The surface tension of liquid X is greater than the surface tension of liquid Y. The viscosity of liquid X is less than the viscosity of liquid Y. 3.arrow_forward4 Discharge, Q through a venturimeter depends on the following variable Inlet pipe diameter - D Throat diameter - d Pressure drop across the venturimeter - Ap Fluid density - P Dynamic viscosity - µ Using MLT set of dimensions evaluate the dimensionless parameters correlating this phenomenon 5 The droplet size, D produced by a liquid spray nozzle depends on the following variable Nozzle diameter - d Jet velocity - U Fluid density - p Dynamic viscosity – u Surface tension - o Using MLT set of dimensions evaluate the dimensionless parameters correlating this phenomenonarrow_forward
- QUESTION 1 Three pipes A, B, and C are interconnected as shown in figure 1. The pipe dimensions are as follows: D (cm) 15 10 20 Pipeline L (m) 300 0.01 B 240 600 0.01 0.005 A 15 m 25 m B Figure 1 1.1 Find the rate at which water will flow in each pipe, ignoring the shock losses at P and entry to pipelines A and B. 1.2 Find the pressure at P.arrow_forwardConsider a pine wood shaft that is 8 ft long and has a diameter of 4 in. 2 What is the volume of the shaft (in ft³)? (Assume the shaft is cylindrical.) x Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. ft3 What is the density of pine wood (see table below)? (Enter your answer in kg/m³.) Density, Specific Gravity, and Specific Weight of Some Materials (at room temperature or at the specified temperature) Material Solids Aluminum Asphalt Cement Clay Fireclay Brick Glass (soda lime) Glass (lead) Glass (Pyrex) Iron (cast) Iron (wrought) Paper Steel (mild) Steel (stainless 304) Wood (ash) Wood (mahogany) Wood (oak) Wood (pine) Density (kg/m³) Specific Gravity Specific Weight (N/m³) 26,880 2,740 2,110 1,920 1,000 1,790 @ 100°C 2,470 4,280 2,230 7,210 7,700 @100°C 930 7,830 7,860 690 550 750 430 2.74 2.11 1.92 1.00 1.79 2.47 4.28 2.23 7.21 7.70 0.93 7.83 7.86 0.69 0.55 0.75 0.43 20,700 18,840 9,810 17,560…arrow_forwardYou are working for a medical device start-up company as a design engineer. Your first task is to make measurements on the flow of blood plasma through your prototype. The device specifications require that 37°C plasma flow into the device pass through a bank of 100 tubes (0.2mm diameter), then exit the device. The total flow rate for the device must be 800 ml min^-1. If you want to maintain a pressure drop across each tube below 100 pascals, what is the maximum length of the tube in centimeters?arrow_forward
- In medical literatures, local blood perfusion rate is typically presented as xx ml/(min 100g tissue), in another word, it represents xx ml of blood supplied to a tissue mass of 100 g per minute to satisfy its nutritional needs. As we learned from the course lectures, the local blood perfusion rate appearing in the Pennes bioheat equation is in a unit of 1/s, or can be interpreted as xx ml of blood supplied to a tissue volume of 1 ml per second. The following lists the blood perfusion rates in various organs or structures in a human body from medical textbooks: brain (50 ml/(min 100g tissue)), kidney (35 ml/(min 100g tissue)), and muscle at rest (3 ml/(min 100g tissue)). Please convert the above local blood perfusion rates into values with the unit of 1/s, therefore, they can be used in the Pennes bioheat equation. The tissue density in a human body is 1050 kg/m³.arrow_forwardb) The variation in the experimental density of water, p, with temperature T, in the range of 20°Carrow_forwardA simple model of blood flow through the descending aorta is provided at the right. Total flow into the aorta is given by Q. The model includes the effects of vessel taper and outflow through 10 tributary arteries, through which the flow is assumed to be equal and given by q. We will assume that the blood is in-viscid and that the flow is steady and laminar. The effects of gravity are neglected. A₁ P₁ A₂ P₂ Find the pressure (P2) at bottom outlet in terms of Q, P₁, and A₁ for the three cases: a) For a tapered vessel for which A2 = A₁/2; and q = 0. b) For a vessel without a taper, but with q = Q/20. c) For a tapered vessel for which A2 = A₁/2 and q = Q/20.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
