The following cell notation contains two half-reactions. Pt | Fe2+ (aq), Fe3+ (aq) || Sn4+ (aq), Sn²+ (aq) | Pt Which of the following statement/equation correctly describes the two half-reactions? anode: Sn4+ (aq)+2e→Sn²+ (aq); cathode: Fe2+(aq)-e→Fe³+(aq); O anode: Fe²+ (aq)-e→Fe³+ (aq); cathode: Sn²+ (aq)+2e→Sn4+ (aq) O anode: Fe³+ (aq)+e→Fe2+ (aq); cathode: Sn²+ (aq)+2e-Sn³+ (aq) anode: Pt + e → Fe³+ (aq)+Fe2+ (aq); cathode: Sn4+ (aq)+Sn²2+ (aq)+2e→Pt O anode: Fe²+ (aq)-e→Fe³+ (aq); cathode: Sn4+ (aq)+2e Sn²+ (aq)
The following cell notation contains two half-reactions. Pt | Fe2+ (aq), Fe3+ (aq) || Sn4+ (aq), Sn²+ (aq) | Pt Which of the following statement/equation correctly describes the two half-reactions? anode: Sn4+ (aq)+2e→Sn²+ (aq); cathode: Fe2+(aq)-e→Fe³+(aq); O anode: Fe²+ (aq)-e→Fe³+ (aq); cathode: Sn²+ (aq)+2e→Sn4+ (aq) O anode: Fe³+ (aq)+e→Fe2+ (aq); cathode: Sn²+ (aq)+2e-Sn³+ (aq) anode: Pt + e → Fe³+ (aq)+Fe2+ (aq); cathode: Sn4+ (aq)+Sn²2+ (aq)+2e→Pt O anode: Fe²+ (aq)-e→Fe³+ (aq); cathode: Sn4+ (aq)+2e Sn²+ (aq)
Chapter18: Introduction To Electrochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 18.18QAP
Related questions
Question
100%
1a

Transcribed Image Text:The following cell notation contains two half-reactions.
Pt | Fe2+ (aq), Fe3+ (aq) || Sn4+ (aq), Sn²+ (aq) | Pt
Which of the following statement/equation correctly describes the two half-reactions?
anode: Sn4+ (aq)+2e→Sn²+ (aq); cathode: Fe2+(aq)-e→Fe³+(aq);
O anode: Fe²+ (aq)-e→Fe³+(aq); cathode: Sn²+ (aq)+2e→Sn4+ (aq)
anode: Fe³+ (aq)+e→Fe2+ (aq); cathode: Sn²+ (aq)+2e→Sn³+ (aq)
anode: Pt + e → Fe³+ (aq)+Fe2+ (aq); cathode: Sn4+ (aq)+Sn²+ (aq) +2e→Pt
O anode: Fe²+ (aq)-e→Fe³+ (aq); cathode: Sn4+ (aq)+2e-Sn²+ (aq)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Using data provided in the table of Standard Potentials, calculate standard emf of the cell described in the last question. Please enter your answer with 2 decimals. for example, 1.056 is written as 1.06. Pay attention to the sign.
this is in par to this question thread
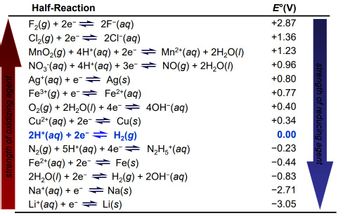
Transcribed Image Text:Half-Reaction
F₂(g) + 2e
2F-(aq)
Cl₂(g) + 2e
2C1-(aq)
MnO₂(g) + 4H+ (aq) + 2e¯ ⇒
NO3(aq) + 4H+ (aq) + 3e¯ ⇒
Ag(s)
Mn²+ (aq) + 2H₂O(l)
NO(g) + 2H₂O(l)
Ag+ (aq) + e
Fe³+ (g) + e
Fe²+ (aq)
O₂(g) + 2H₂O(l) + 4e¯ ⇒ 4OH¯(aq)
Cu²+ (aq) + 2e → Cu(s)
2H*(aq) + 2e = H₂(g)
N₂H5*(aq)
N₂(g) + 5H+(aq) + 4e¯⇒
Fe²+ (aq) + 2e → Fe(s)
2H₂O(l) + 2e → H₂(g) + 2OH(aq)
Na+ (aq) + e
Na(s)
Li+ (aq) +eLi(s)
E°(V)
+2.87
+1.36
+1.23
+0.96
+0.80
+0.77
+0.40
+0.34
0.00
-0.23
-0.44
-0.83
-2.71
-3.05
strength of reducing agent
Solution
Follow-up Question
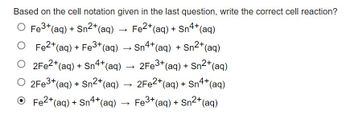
Transcribed Image Text:Based on the cell notation given in the last question, write the correct cell reaction?
O Fe³+ (aq) + Sn²+ (aq)
O Fe²+ (aq) + Fe3+ (aq)
O 2Fe2+ (aq) + Sn4+ (aq)
O 2Fe3+ (aq) + Sn²+ (aq)
Fe2+ (aq) + Sn4+ (aq)
Fe2+ (aq) + Sn4+ (aq)
› Sn4+ (aq) + Sn2+ (aq)
2Fe3+ (aq) + Sn2+ (aq)
2Fe2+ (aq) + Sn4+ (aq)
Fe3+ (aq) + Sn²+ (aq)
O
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning