Reaction Conc. Na2S203 Conc. HCI A Abs. A Time (s) Rate (A Abs./BA Time) 1.3686611 1.5360817 1.2267196 0.9563164 1.007568 0.300349 0.01870913 0.02870913 .30 M .15 M 1 0.10 M 1.358380874 2 0.10 M 5.114311671 .30 M .30 M 3 0.050 M 65.56796601 4 0.025 M 11.3085840 Use experimental data and the rate law to calculate a rate constant for each reaction 1, 2, 3, 4. How do the rate constants compare? Should they be the same or different? Discuss in your conclusions. Report the average value of your calculations. Be sure to include units in your rate constant. The rate law of the reaction is shown below: Rate = [NazS203]¬2
Reaction Conc. Na2S203 Conc. HCI A Abs. A Time (s) Rate (A Abs./BA Time) 1.3686611 1.5360817 1.2267196 0.9563164 1.007568 0.300349 0.01870913 0.02870913 .30 M .15 M 1 0.10 M 1.358380874 2 0.10 M 5.114311671 .30 M .30 M 3 0.050 M 65.56796601 4 0.025 M 11.3085840 Use experimental data and the rate law to calculate a rate constant for each reaction 1, 2, 3, 4. How do the rate constants compare? Should they be the same or different? Discuss in your conclusions. Report the average value of your calculations. Be sure to include units in your rate constant. The rate law of the reaction is shown below: Rate = [NazS203]¬2
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter11: Chemical Kinetics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11.49PAE: The rate of photodecomposition of the herbicide piclo- ram in aqueous systems was determined by...
Related questions
Question
![Reaction
Conc. Na2S½O3 Conc. HCI
A Abs.
A Time (s)
Rate
(A Abs./ga Time)
1.007568
0.300349
0.01870913
0.02870913
1
0.10 M
.30 М
1.3686611
1.358380874
0.10 M
.15 M
1.5360817
5.114311671
3
0.050 M
.30 M
1.2267196
65.56796601
4
0.025 M
.30 M
0.9563164
11.3085840
4. Use experimental data and the rate law to calculate a rate constant for each reaction 1, 2, 3, 4.
How do the rate constants compare? Should they be the same or different? Discuss in your
conclusions. Report the average value of your calculations. Be sure to include units in your
rate constant.
The rate law of the reaction is shown below:
Rate =
[Na2S2O3]-2](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Ff1aaab1d-8ba4-46f3-ada9-df467e4ce664%2Ffeed4d2b-cc59-42b1-bfde-af19d1c6f2df%2Fniqm70n_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Reaction
Conc. Na2S½O3 Conc. HCI
A Abs.
A Time (s)
Rate
(A Abs./ga Time)
1.007568
0.300349
0.01870913
0.02870913
1
0.10 M
.30 М
1.3686611
1.358380874
0.10 M
.15 M
1.5360817
5.114311671
3
0.050 M
.30 M
1.2267196
65.56796601
4
0.025 M
.30 M
0.9563164
11.3085840
4. Use experimental data and the rate law to calculate a rate constant for each reaction 1, 2, 3, 4.
How do the rate constants compare? Should they be the same or different? Discuss in your
conclusions. Report the average value of your calculations. Be sure to include units in your
rate constant.
The rate law of the reaction is shown below:
Rate =
[Na2S2O3]-2
Expert Solution
Introduction
The rate of a reaction can be defined as the rate of decrease in concentration of reactants or the rate of increase in concentration of product.
The rate law can be expressed in terms of powers of concentration of reactants, and the reaction constant K.
That is
For this simple reaction
nA→B
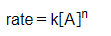
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning