Accounts Debit Credit Cash $24,300 Accounts Receivable 42,500 Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts $2,700 Inventory 42,000 Land 79,600 Accounts Payable 29,200 Notes Payable (8%, due in 3 years) 42,000 Common Stock 68,000 Retained Earnings 46,500 Totals $188,400 $188,400
Accounts Debit Credit Cash $24,300 Accounts Receivable 42,500 Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts $2,700 Inventory 42,000 Land 79,600 Accounts Payable 29,200 Notes Payable (8%, due in 3 years) 42,000 Common Stock 68,000 Retained Earnings 46,500 Totals $188,400 $188,400
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Makers
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305654174
Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Chapter7: Receivables And Investments
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.1DC: Reading 3M Companys Balance Sheet: Accounts Receivable The following current asset appears on the...
Related questions
Question
![Accounts
Debit
Credit
Cash
$24,300
Accounts Receivable
42,500
Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts
$2,700
Inventory
42,000
Land
79,600
Accounts Payable
29,200
Notes Payable (8%, due in 3 years)
42,000
Common Stock
68,000
Retained Earnings
46,500
Totals
$188,400
$188,400
The $42,000 beginning balance of inventory consists of 420 units, each costing $100. During January 2024, Big Blast
Fireworks had the following inventory transactions:
January 3 Purchase 1,050 units for $115,500 on account ($110 each).
January 8 Purchase 1,150 units for $132,250 on account ($115 each).
January 12 Purchase 1,250 units for $150,000 on account ($120 each).
January 15 Return 160 of the units purchased on January 12 because of defects.
January 19 Sell 3,600 units on account for $576,000. The cost of the units sold is determined using a FIFO perpetual
inventory system.
January 22 Receive $529,000 from customers on accounts receivable.
January 24 Pay $359,000 to inventory suppliers on accounts payable.
January 27 Write off accounts receivable as uncollectible, $2,100.
January 31 Pay cash for salaries during January, $110,000.
The following information is available on January 31, 2024.
a. At the end of January, the company estimates that the remaining units of inventory purchased on January 12 are
expected to sell in February for only $100 each. [Hint: Determine the number of units remaining from January 12 after
subtracting the units returned on January 15 and the units assumed sold (FIFO) on January 19.]
b. The company records an adjusting entry for $5,070 for estimated future uncollectible accounts.
c. The company accrues interest on notes payable for January. Interest is expected to be paid each December 31.
d. The company accrues income taxes at the end of January of $13,500.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fa67304b1-3709-41d7-a763-4eb6f13a6e63%2Fc553be45-1887-4511-93f0-b3ebd023d349%2Fdq9fivw_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Accounts
Debit
Credit
Cash
$24,300
Accounts Receivable
42,500
Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts
$2,700
Inventory
42,000
Land
79,600
Accounts Payable
29,200
Notes Payable (8%, due in 3 years)
42,000
Common Stock
68,000
Retained Earnings
46,500
Totals
$188,400
$188,400
The $42,000 beginning balance of inventory consists of 420 units, each costing $100. During January 2024, Big Blast
Fireworks had the following inventory transactions:
January 3 Purchase 1,050 units for $115,500 on account ($110 each).
January 8 Purchase 1,150 units for $132,250 on account ($115 each).
January 12 Purchase 1,250 units for $150,000 on account ($120 each).
January 15 Return 160 of the units purchased on January 12 because of defects.
January 19 Sell 3,600 units on account for $576,000. The cost of the units sold is determined using a FIFO perpetual
inventory system.
January 22 Receive $529,000 from customers on accounts receivable.
January 24 Pay $359,000 to inventory suppliers on accounts payable.
January 27 Write off accounts receivable as uncollectible, $2,100.
January 31 Pay cash for salaries during January, $110,000.
The following information is available on January 31, 2024.
a. At the end of January, the company estimates that the remaining units of inventory purchased on January 12 are
expected to sell in February for only $100 each. [Hint: Determine the number of units remaining from January 12 after
subtracting the units returned on January 15 and the units assumed sold (FIFO) on January 19.]
b. The company records an adjusting entry for $5,070 for estimated future uncollectible accounts.
c. The company accrues interest on notes payable for January. Interest is expected to be paid each December 31.
d. The company accrues income taxes at the end of January of $13,500.
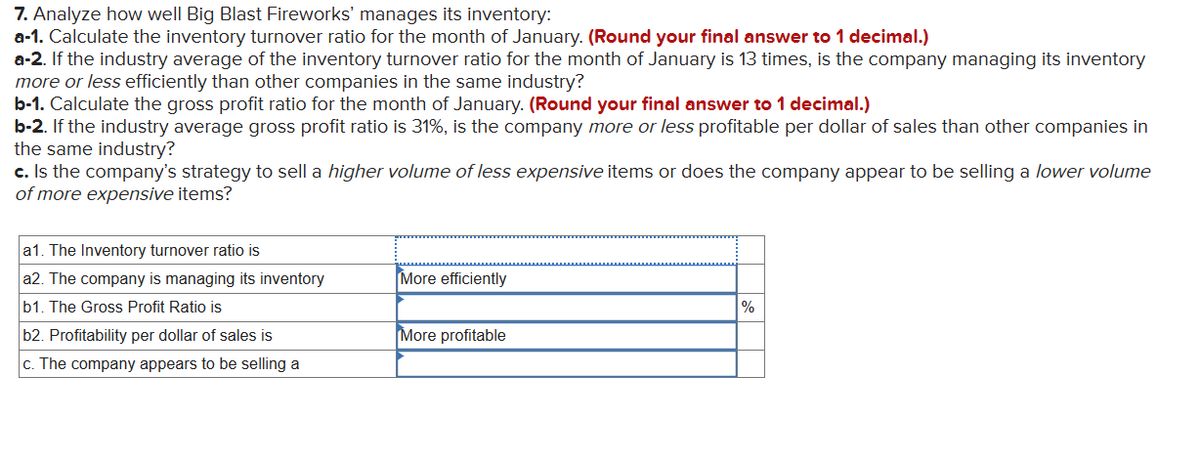
Transcribed Image Text:7. Analyze how well Big Blast Fireworks' manages its inventory:
a-1. Calculate the inventory turnover ratio for the month of January. (Round your final answer to 1 decimal.)
a-2. If the industry average of the inventory turnover ratio for the month of January is 13 times, is the company managing its inventory
more or less efficiently than other companies in the same industry?
b-1. Calculate the gross profit ratio for the month of January. (Round your final answer to 1 decimal.)
b-2. If the industry average gross profit ratio is 31%, is the company more or less profitable per dollar of sales than other companies in
the same industry?
c. Is the company's strategy to sell a higher volume of less expensive items or does the company appear to be selling a lower volume
of more expensive items?
a1. The Inventory turnover ratio is
a2. The company is managing its inventory
b1. The Gross Profit Ratio is
More efficiently
%
More profitable
c. The company appears to be selling a
b2. Profitability per dollar of sales is
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step 1: Define 'Ratio analysis':
VIEWStep 2: Working Notes:
VIEWStep 3: (7-a-1) Determine the inventory turnover ratio for the month of January:
VIEWStep 4: (7-a-2) Comment on the performance of the company:
VIEWStep 5: (7-b-1) Determine the gross profit for the month of January:
VIEWStep 6: (7-b-2) Comment on the performance of the company:
VIEWStep 7: (7-c) Explain the company strategy:
VIEWSolution
VIEWStep by step
Solved in 8 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning